Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Chapter 5). The AM hyphae increase the nutrient-absorbing surface of the root
and may prolong its absorbing life. Also, the suberized exodermis, by
preventing the death of cortical cells in drought, may provide a protected
environment for AM as well as giving protection from pathogens and pests
(Peterson, 1992).
Apart from very young seedlings, the bulk of the root system is made up of
the adventitious roots which originate in the primary thickening meristem
near the top of the stem (see Figs 2.5 and 2.10). These emerge from all sides of
the stem and tend to grow near horizontally for some distance before turning
downwards.
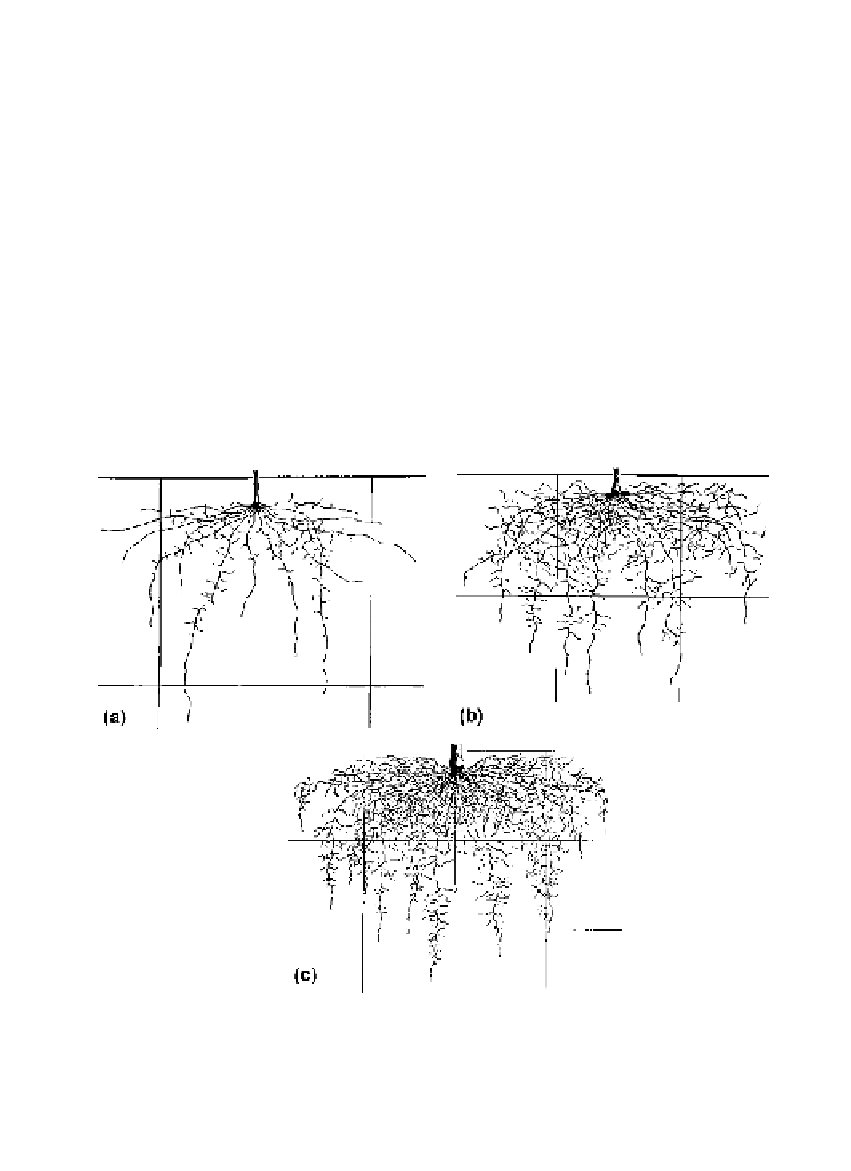
Laborious investigations of root development in onion, leek and garlic were
made by Weaver and Brunner (1927). All three crops have similar root
systems, and Fig. 2.15 shows the leek root system at various stages of
development. The roots vary between 2.0 and 0.5 mm in thickness and are
fairly sparsely branched, with one to two lateral branches per cm of primary
Fig. 2.15.
Stages in the development of the root system of leek plants grown in
rows 1 m apart with 10 cm between plants within the rows. Seeds were sown in
mid-March in a well-structured loam at Norman, Oklahoma, USA: (a) roots of 2-
month-old plant; (b) half of the roots of a 3-month-old plant; (c) 25% of the roots of
a 4.5-month-old plant. The scale lines show a 30 cm (1 foot) square grid (from Figs
11, 12 and 13 of Weaver and Brunner, 1927).