Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
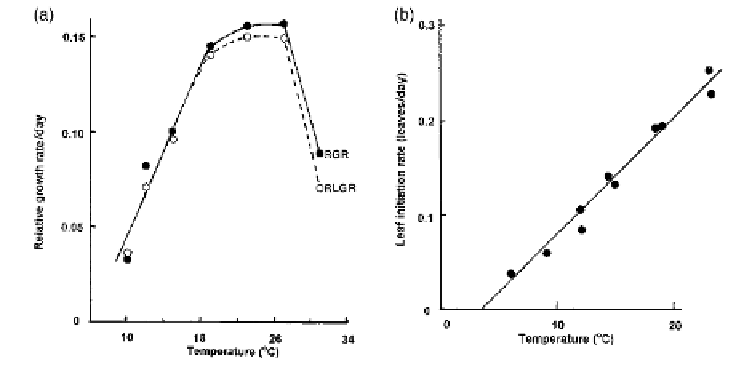
Fig. 4.22.
(a) The effect of temperature on the Relative Growth Rate (RGR) of whole
plant dry weight (solid symbols) and on the Relative Leaf Growth Rate (RLGR)
(open symbols) of cv. 'Hygro' during early exponential growth (from Brewster,
1979). RGR is the rate of increase in dry weight per unit of existing dry weight
(RGR = 1/W.dW/dt, where W = dry weight and t = time). Similarly, RLGR is the rate
of increase of leaf area per unit of existing leaf area. (b) The effect of temperature
on the rate of initiation of leaves by the main shoot apex (i.e. not counting leaves
on side shoots) of cvs 'Hygro', 'Hyton' and 'Rijnsburger', all 'Rijnsburger' types,
growing in controlled environments (unpublished data).
Scaife
et al.
(1987). Here, 'Effective Day Degrees' (EDD) are used instead of day-
degrees (DD) in Eqn 4.17b:
log
e
(Dry Weight) = log
e
(W
0
) + p
EDD
(Eqn 4.18)
where p is a parameter that expresses relative growth per EDD and has
units per EDD.
An 'Effective Day Degree' is a day-degree adjusted or weighted for the daily
total PAR impinging on the plants (termed the 'radiant exposure to PAR').
EDDs are calculated according the equation:
EDD
-1
= DD
-1
+ f
R
-1
(Eqn 4.19a)
this can be also expressed in the equivalent form:
EDD = DD/(1 + (f
DD)/R) (Eqn 4.19b)
R is the daily radiant exposure to photosyntetically active radiation,
usually expressed as MJ/m
2
f is a parameter that determines sensitivity to PAR levels and has units
MJ/m
2
/DD.
Parameters p and f are characteristic of a species. From experiments under
controlled PARs and temperatures, the value for onion of p was 0.0160/EDD, f