Database Reference
In-Depth Information
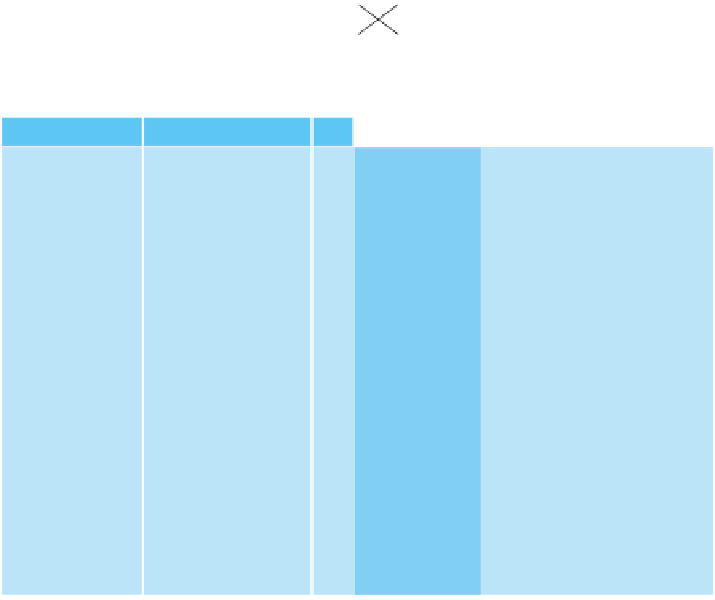
Unauthorized access also includes users who have legitimate access to some but not all data in a database
and who attempt to access data for which they are not authorized. For example, the DBMS prevents Paige
from accessing customer balances, as shown in Figure 8-6, because the DBA did not grant her access privi-
leges to that data.
DBMS prevents Paige
from accessing
customer balances
A uthorized
user
DBMS
261
Paige
Customer
CustomerNum
CustomerName
...
Balance
CreditLimit
RepNum
148
Al's Appliance
...
$6,550.00
$7,500.00
20
and Sport
282
Brookings Direct
...
$431.50
$10,000.00
35
356
Ferguson's
...
$5,785.00
$7,500.00
65
408
The Everything
...
$5,285.25
$5,000.00
35
Shop
462
Bargains Galore
...
$3,412.00
$10,000.00
65
524
Kline's
...
$12,762.00
$15,000.00
20
608
Johnson's
...
$2,106.00
$10,000.00
65
Department
Store
687
Lee's Sport and
...
$2,851.00
$5,000.00
35
Appliance
725
Deerield's Four
...
$248.00
$7,500.00
35
Seasons
842
All Season
...
$8,221.00
$7,500.00
20
FIGURE 8-6
Attempted security violation by Paige, who's authorized to access some customer data but is not authorized
to access customer balances
The DBA takes the steps necessary to ensure that the database is secure. After the DBA determines the
access privileges for each user, the DBA creates security policies and procedures, obtains management
approval of the policies and procedures, and then distributes them to authorized users.
To implement and enforce security, the DBA uses the DBMS
s security features, such as encryption,
authentication, authorizations, and views. If a DBMS lacks essential security features, the DBA might create or
purchase special security programs that provide the missing features.
In addition to relying on the security features provided by the DBMS and, if necessary, the special secu-
rity programs, the DBA monitors database usage to detect potential security violations. If a security violation
occurs, the DBA determines who breached security, how the violation occurred, and how to prevent a similar
violation in the future.
'
Disaster Planning
The type of security discussed in the previous section concerns damage to the data in a database caused by
authorized and unauthorized users. Damage to a database can also occur through a physical incident such as
an abnormally terminated program, a software virus or worm, a disk problem, a power outage, a computer
malfunction, a hurricane, a flood, a tornado, or another natural disaster.