Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
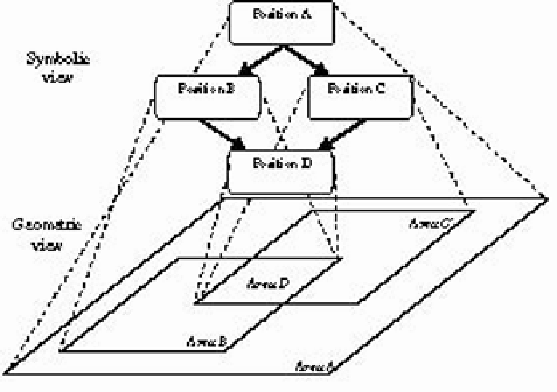
Figure 4: Semi-symbolic representation model.
Figure 4: Semi-symbolic representation model.
3.2
Absolute versus relative position
Based on the reference points used by a positioning system, it can be
classified as
absolute
or
relative
.
An absolute positioning system uses a universal grid reference to estimate
the position of objects. For example, all GPS-based systems use the latitude,
longitude and altitude to represent the position.
In a relative positioning system, each mobile object can have its own
reference system. For example, during military actions, each soldier may
know the position of companions as to his/her own position.
An absolute position can be transformed into a relative position (as to a
second reference point) and vice versa. The triangulation is used for the
determination of an absolute position from multiple relative readings if the
absolute position of landmarks is well known.
However, often reference points position may not be known or reference
points can be mobile themselves. As a consequence, when a positioning
system is classified as absolute or relative, actually the classification is
related to what information is available and how the system uses it, rather
than any intrinsic property of the system.
3.3
Accuracy versus precision
A positioning system should return the position of objects to locate
accurately and independently from the measurement units. Some inexpensive