Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
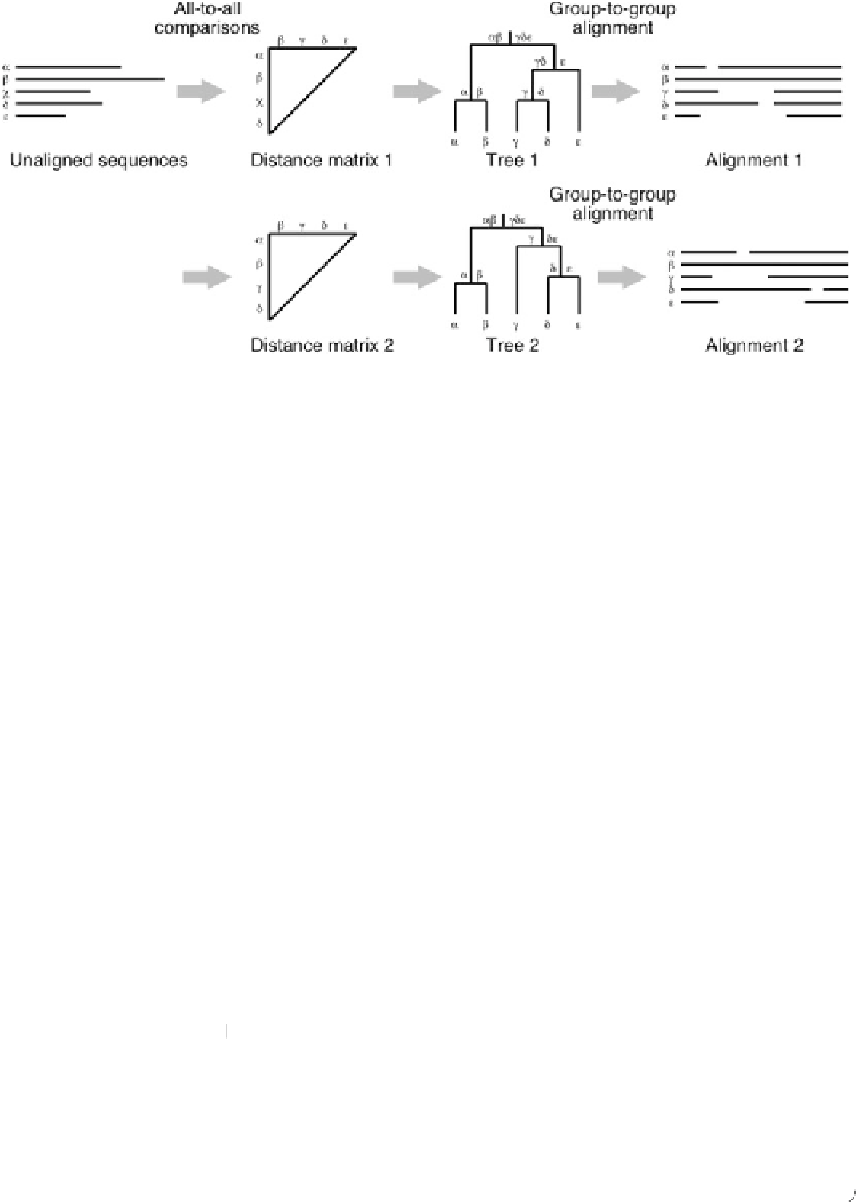
Fig. 1 Calculation procedure for the progressive options (reprinted from [
57
])
MAFFT assumes that the sequences involved in an MSA are
homologous, that is, sharing a single common ancestral sequence.
MAFFT always generates an MSA that has all the letters of the input
sequences. The order of the letters in each sequence is identical to
that of the input sequence, although the sequences can be reor-
dered according to similarity.
The progressive method [
9
,
10
] is the most basic MSA algorithm.
A guide tree is created based on all-to-all pairwise comparisons, and
an MSA is constructed using a group-to-group alignment algo-
rithm at each node of the guide tree. To achieve a reasonable
balance between speed and accuracy, MAFFT uses a two-cycle
progressive method, FFT-NS-2, shown in Fig.
1
. First, low-
quality all-pairwise distances are rapidly calculated, based on the
number of shared
k
mers, to build an initial tree [
11
].
k
is 6 for both
protein and nucleotide sequences as noted in [
1
]. A tentative MSA
is computed using the initial guide tree, and then a refined tree is
built using the tentative MSA. Finally, an MSA is constructed based
on the refined tree. This is the default option
2.1 Progressive
Methods
A faster option, FFT-NS-1, which performs the first cycle only, is
also available.