Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
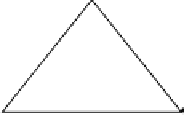
O
p
r
h
s
s
2
2
s
A
B
Fig. 12.1.
One of the isosceles triangles forming a regular polygon.
If we let
s
= 1 the following table shows the area for the first six polygons.
n
Area
3
0.433
4
1
5
1.72
6
2.598
7
3.634
8
4.828
12.2 Calculate the Area of any Polygon
Figure 12.2 shows a polygon with the following vertices in counter-clockwise
sequence.
x
0
2
5
4
2
y
2
0
1
3
3
By inspection, the area is 9.5.
The area of a polygon is given by
n−
1
x
i
y
i
+1(mod
n
)
−
y
i
x
i
+1(mod
n
)
area =
1
2
i
=0
area =
1
2
(0
×
0+2
×
1+5
×
3+4
×
3+2
×
2
−
2
×
2
−
0
×
5
−
1
×
4
−
3
×
2
−
3
×
0)
area =
1
2
(33
−
14) = 9
.
5
12.3 Calculate the Dihedral Angle of a Dodecahedron
The dodecahedron is a member of the five Platonic solids, which are con-
structed from regular polygons. The dihedral angle is the internal angle
between two faces. Figure 12.3 shows a dodecahedron with one of its pen-
tagonal sides.