Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
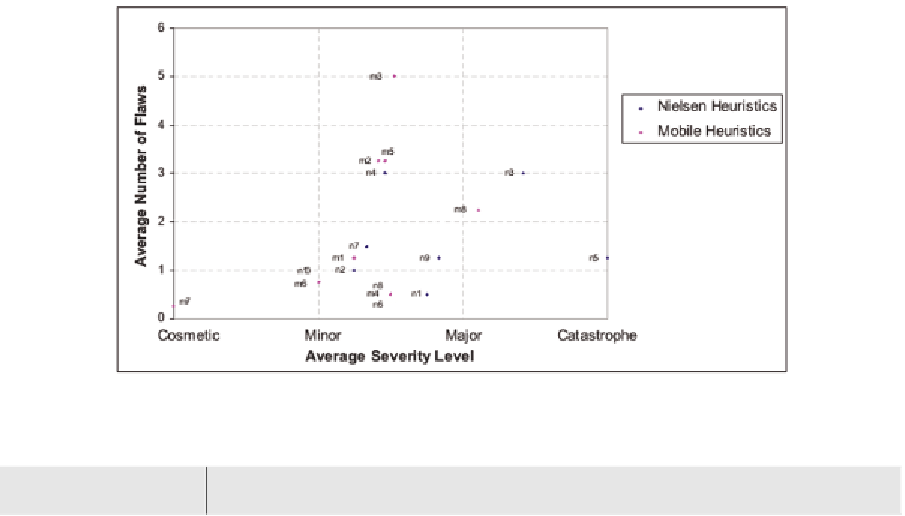
Figure 6. Comparison of the sets of heuristics: flaws and severity
Table 3. Nielsen's heuristics and corresponding usability problems
Number of Usability
Problems
Nielsen's Heuristics 1-10
Description of Heuristic
4
12
Consistency and standards
3
12
User control and freedom
7
6
Flexibility and efficiency of use
9
5
Help users recognize, diagnose, and recover from errors
5
5
Error prevention
2
4
Match between system and the real world
10
3
Help and documentation
1
2
Visibility of system status
6
2
Recognition rather than recall
8
2
Aesthetic and minimalist design
could be applied after Nielsen's heuristics. It is
worth recalling that there are some problems that
Nielsen's heuristics failed to identify (based on
Table 1). Some might now be identified by mobile
heuristics and might lie between Minor and Ma-
jor severity levels (Table 2 and Figure 4).
•
Nielsen's heuristics: Nielsen's heuristic 4
(12 times), Nielsen's heuristic 3 (12 times).
The foregoing are [each] less than any of
the following mobile heuristics.
•
Mobile heuristics: mobile heuristic 3 (20
times), mobile heuristic 5 (13 times), mo-
bile heuristic 2 (13 times).
Usability Flaws and Heuristics
It is interesting to observe that these high-
lighted Nielsen's heuristics (4 [Consistency and
standards], 3 [User control and freedom]) are
related to the highlighted mobile heuristics (3
As seen in Table 3 and Table 4, the most frequently
used/highlighted heuristics in the mobile applica-
tions are as follows
6
:

















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search