Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
on mobiles
than
Mobile Internet
. The different
alternatives for using and accessing the Web on
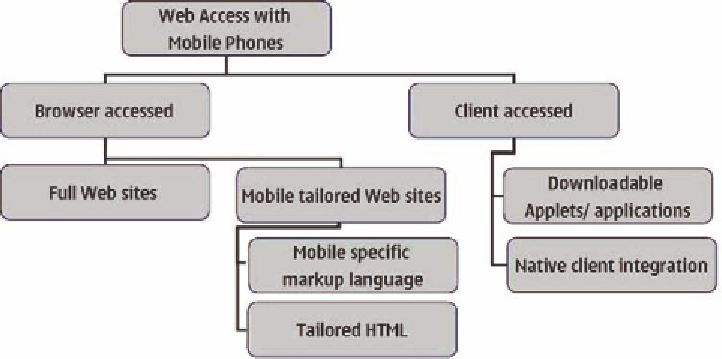
mobiles today can be seen in Figure 1. Web access
from mobiles can be divided to
browser-accessed
and
client-accessed
. The difference is very clear
from the user's perspective. For browser-accessed
approaches, there are two alternatives; a site can be
either identical to that which the user accesses via
a desktop computer or the content can be tailored
for a mobile platform. Client-access means that
applications connect to a service to fetch specific
pieces of data from the Web: different approaches
support different usage situations, and therefore
one service can be accessed multiple ways.
therefore, look awkward on mobile (or other)
browsers to a user who is familiar with the site on
a specific browser on a desktop computer.
Full Web content on mobile devices is not
really a new thing; it has been possible to access
full Web content on mobiles for as long as it has
been possible to access mobile-tailored content;
for example, the Nokia Communicator provided
a Web browser with HTML support as early as
the late 90s. Kaasinen
et al
. (2000) demonstrated
ways to render Web content to fit the screen of a
mobile phone, and Roto and Kaikkonen (2003)
analyzed the problems users have when full pages
are rendered to a narrow layout inside mobile
browsers. Currently the narrow layout is no longer
the only solution; as mobile phone screens have
become bigger; more devices are able to show
the Web site layout in a comparable manner to
the layout seen on a desktop computer. Figure 2A
shows how one service,
Share on Ovi
(a full Web
page), looks on a mobile device. I will explain the
other figures in the following sections.
Lately, increasing numbers of companies have
started to take mobile browsers into consideration
when building their full Web sites. The question
now is '
how do you best create Web sites that fit
both desktop computers and mobile devices?
'.
For example, Yahoo! has defined guidelines to
Full Web on Mobile Phones
Full Web sites are sites developed with standard
HTML for desktop computer use. The content on
a mobile browser is (with some technical limita-
tions) the same as that which the user sees when
browsing the site on a desktop computer. Most
mobile browsers do not support all audio and
video formats; this means that a user may not be
able to listen to background music or view video
clips on sites. In some cases full Web site design
is optimized for a specific browser, commonly
Internet Explorer. The layout of such sites may,
Figure 1. Landscape of the mobile Internet
Search WWH ::

Custom Search