Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
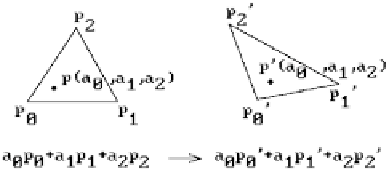
Figure 11.21.
Affine maps preserve barycen-
tric coordinates.
11.5.2.1
Theorem.
(The
Polar Form
or
Blossoming Theorem
) Let
m
p
:
RR
Æ
be a polynomial function of degree d. Then there exists a
unique
symmetric multi-
affine map
d m
:
RR
P
Æ
satisfying P(u, ...,u) = p(u). Furthermore, the rth derivative of p is given by
r
d
dr
!
r
i
Ê
Ë
ˆ
¯
Â
ri
-
(
)
r
()
=
()
pu
1
Pu
( ,..., ,
u u
+
1
,...,
u
+
1
).
(11.87)
1441 2
443
44
(
)
-
!
i
=
0
di
-
i
The map P is called the
polar form
or
blossom
of p.
Proof.
See [Rams88]. Express p in the form
d
d
i
Ê
Ë
ˆ
¯
Â
a
0
i
()
=
pu
u
,
i
i
=
where
a
i
Œ
R
m
, and let
d
Â
a
s
(
)
=
(
)
Pu u
,
,...,
u
u u
,
,...,
u
,
12
d
i
i
12
d
i
=
0
where s
i
=s
i
(u
1
,u
2
,...,u
d
) is the ith elementary symmetric polynomial in the
variables u
1
, u
2
,..., u
d
. It is easy to check that
(
)
=
()
Pu
,...,
u
pu
.
Next, let d :
R
Æ
R
d
be the diagonal map
()
=
(
)
du
u
,...,
u
.
Then p(u) = P(d(u)). Therefore, by the chain rule