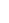Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
isolated, the master locks another i le used by vSphere HA on the heartbeat datastore. When the
isolated node sees that this i le has been locked by a master, it knows that the master is assum-
ing responsibility for restarting the VMs—remember that only a master can restart VMs—and
the isolated host is then free to execute the coni gured isolation response. Therefore, even if the
isolation response is set to Shut Down or Power Off, that action won't take place until the iso-
lated slave has coni rmed, via the datastore heartbeating structures, that a master has assumed
responsibility for restarting the VMs.
The question still remains, though: Should I change the Host Isolation Response setting?
The answer to this question is highly dependent on the virtual and physical network infra-
structures in place. Let's look at a couple of examples.
Let's say we have a host in which both the ESXi management network and the VM networks
are connected to the same virtual switch bound to a single network adapter (clearly not a gener-
ally recommended coni guration). In this case, when the cable for the uplink on this vSwitch is
unplugged, communication to the ESXi management network and every VM on that computer
is lost. The solution, then, should be to shut down the VMs. When an ESXi host determines it
is isolated and has coni rmed that a master host has assumed responsibility for restarting the
VMs, it can execute the isolation response so that the VMs can be restarted on another host with
full network connectivity.
A more realistic example might be a situation in which a single vSwitch has two uplinks, but
both uplinks go to the same physical switch. If this vSwitch hosts both the ESXi management
and VM networks, then the loss of that physical switch means that both management trafi c and
VM trafi c have been interrupted. Setting Host Isolation Response to Shut Down would allow
vSphere HA to restart those VMs on another ESXi host and restore connectivity to the VMs.
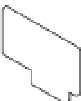
However, a network coni guration that employs multiple uplinks, multiple vSwitches,
and multiple physical switches, as shown in Figure 7.22, should probably leave Host Isolation
Response set to Leave Powered On because it's unlikely that a network isolation event would
also leave the VMs on that host inaccessible.
Figure 7.22
h e option to leave
VMs running when
a host is isolated
should be set only
when the virtual
and the physical
networking infra-
structures support
high availability.
ESXi Host
Management
traffic
vMotion
traffic
Virtual machine
traffic
vSwitch0
vSwitch1
Network
switch
Redundant
switch