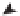Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
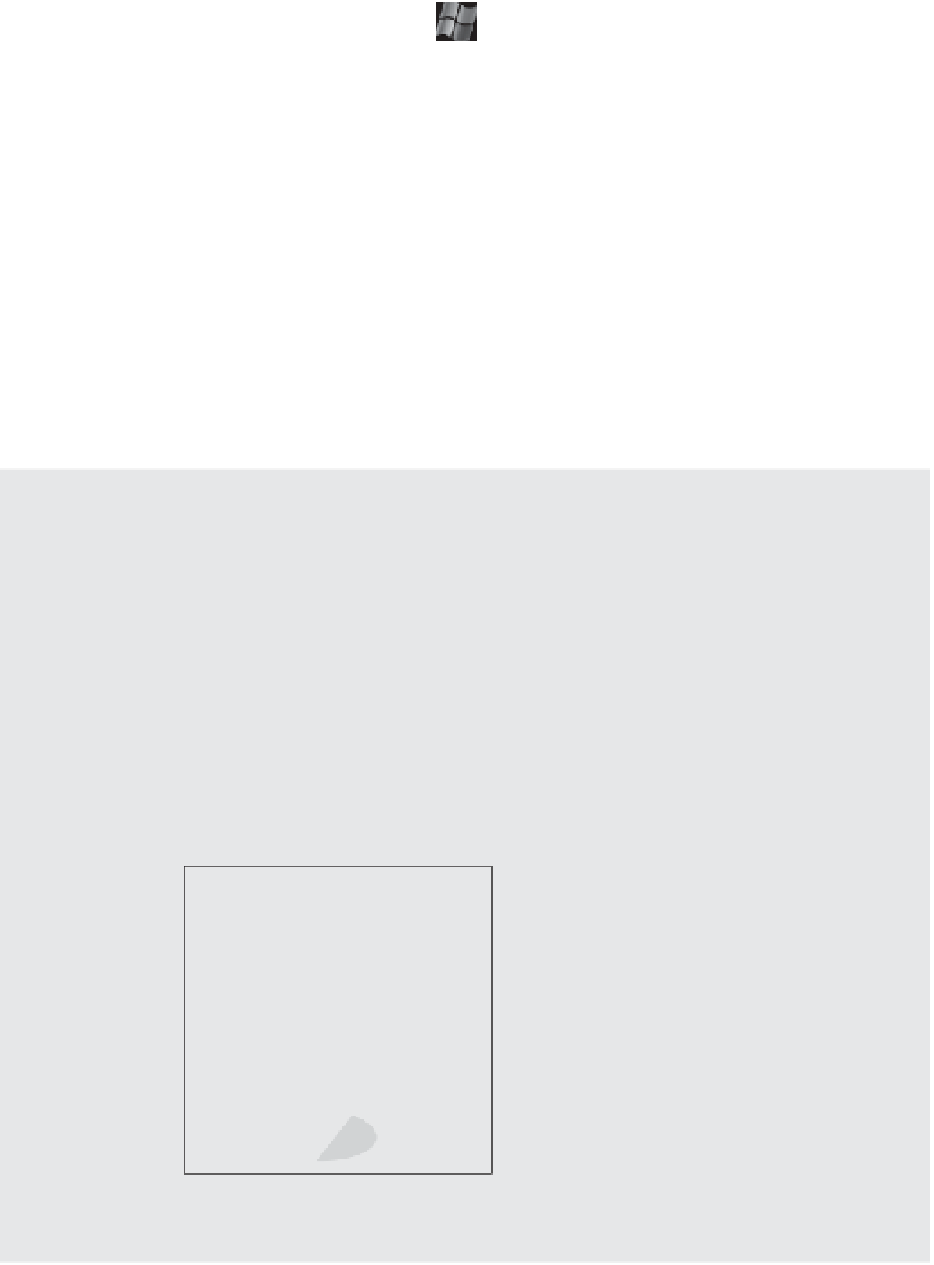
Figure 7.5
A Microsoft cluster
built on VMs resid-
ing on separate
ESXi hosts requires
shared storage
access from each
VM using an RDM.
esxi-06.lab.local
esxi-08.lab.local
VM1
VM2
This virtual switch carries private
(heartbeat) traffic between the
cluster nodes.
vSwitch
vSwitch
vSwitch
vSwitch
This virtual switch carries public
(production) traffic to and from
the cluster nodes.
Shared
datastore
Using Raw Device Mappings in Your Virtual Clusters
An RDM is not a direct access to a LUN, and it is not a normal virtual hard disk fi le. An RDM is a
blend of the two. When you're adding a new disk to a VM, as you will soon see, the Add Hardware
Wizard presents the RDMs as an option on the Select A Disk page. h is page defi nes the RDM as
having the ability to give a VM direct access to the SAN, thereby allowing SAN management. We
know this seems like a contradiction to the opening statement of this sidebar; however, we're get-
ting to the part that, oddly enough, makes both statements true.
By selecting an RDM for a new disk, you're forced to select a compatibility mode for the RDM. An
RDM can be confi gured in either Physical Compatibility mode or Virtual Compatibility mode. h e
Physical Compatibility mode option allows the VM to have direct raw LUN access. h e Virtual
Compatibility mode, however, is the hybrid confi guration that allows raw LUN access but only
through a VMDK fi le acting as a proxy. h e following image details the architecture of using an
RDM in Virtual Compatibility mode.
esxi-05.lab.local
Raw device mapping
file resides on VMFS
and points to separate
LUN
R:\ points to win2k8r2-01_1.vmdk
C:\ points to win2k8r2-01.vmdk
VMFS
NTFS