Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
The array service time itself is a function of many things, predominantly the workload, then
the spindle coni guration, then the write cache (for writes only), then the storage processors, and
i nally, with certain rare workloads, the read caches.
So why is all this important? Well, for most customers it will never come up, and all queuing
will be happening behind the scenes. However, for some customers, LUN queues determine
whether your VMs are happy or not from a storage performance perspective.
When a queue overl ows (either because the storage coni guration cannot handle the steady-
state workload or because the storage coni guration cannot absorb a burst), it causes many
upstream effects to slow down the I/O. For IP-focused people, this effect is analogous to TCP
windowing, which should be avoided for storage just as queue overl ow should be avoided.
You can change the default queue depths for your HBAs and for each LUN/device. (See
www
.vmware.com f
or HBA-specii c steps.) After changing the queue depths on the HBAs, you need
to perform a second step at the VMkernel layer. You must change the amount of outstanding
disk requests from the VMs to VMFS to match the HBA setting. You can do this in the ESXi
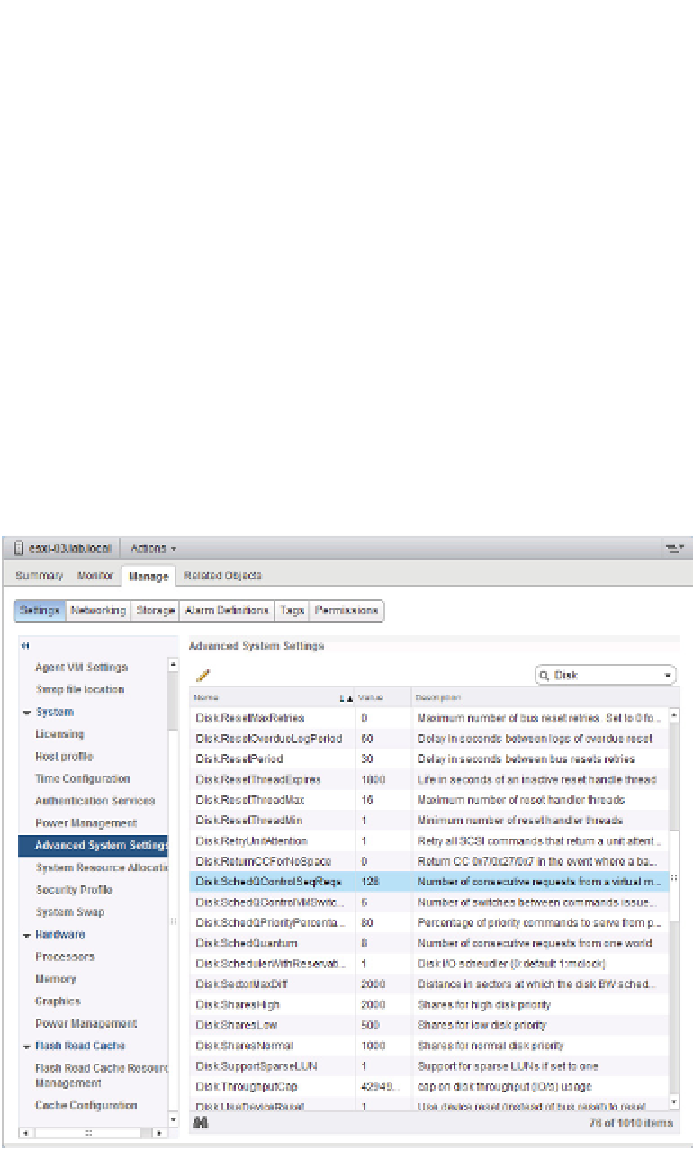
advanced settings, as shown in Figure 6.22 or by using ESXCLI. In general, the default set-
tings for queues and Disk.* are the best. We don't recommend changing these values unless
instructed to do so by VMware or your storage vendor.
Figure 6.22
It is possible to
adjust the advanced
properties for
advanced use cases,
increasing the num-
ber of consecutive
requests allowed
to match adjusted
queues.
If the queue overl ow is not a case of dealing with short bursts but rather that you are under-
coni gured for the steady state workload, making the queues deeper can have a downside:
higher latency. Then it overl ows anyway. This is the predominant case, so before increasing
your LUN queues, check the array service time. If it's taking more than 10 milliseconds to ser-
vice I/O requests, you need to improve the service time, usually by adding more spindles to the
LUN or by moving the LUN to a faster-performing tier.