Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
dag2
dag3
ANL
ANL
STAT
ALG
S TAT
ALG
MECH
MECH
VECT
VECT
cpdag(dag2)
cpdag(dag3)
ANL
ANL
STAT
ALG
S TAT
ALG
MECH
MECH
VECT
VECT
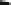
Fig. 2.3
Two net works (
dag2
and
dag3
) derived from
dag
, with different sets of v-structures
and therefore belonging to different equivalence classes (
cpdag(dag2)
and
cpdag(dag3)
).
Both these networks have the same moral graph as
dag
, shown in the
right panel
of Fig.
2.2
.
V-structures are highlighted with a
thicker line width
catNetwork
in
catnet
), describing a Bayesian network as a whole. This design
choice makes network structures not as easy to modify as in
bnlearn
, because the
parameters of the local distributions must be modified at the same time to preserve
the coherence of the
R
object. Furthermore, in some cases the lack of accessor func-
tions forces the user to work directly on the internals of the class, which increases
the complexity of even simple tasks. On the other hand, class
pcAlgo
from
pcalg
stores the network structure in an object of class
graphNEL
, making it possible to
use all the functions provided by the
graph
package (
Gentleman et al.
,
2012
).
Consider, for instance, the undirected graph and the DAG shown in Fig.
2.2
. With
the
deal
package we can again create an empty network, which in this case is an
object of class
network
.
> library(deal)
> deal.net = network(marks)
> deal.net
## 5 ( 0 discrete+ 5 ) nodes;score= ;relscore=
1
MECH continuous()
2
VECT continuous()















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search