Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
processes, that is, processes such as DNA replication, transcription and translation.
The bacterial-related genes, in contrast, encode proteins involved in metabolic pro-
cesses such as respiration and photosynthesis - operational processes. The startling
conclusion is that eukaryotes are descended from hybrids of Archaea and Bacteria
- all life is microbial!
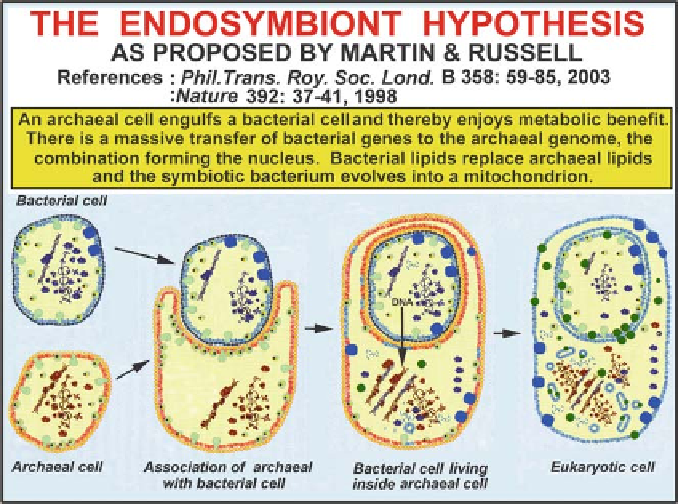
There is much current debate as to precisely how archaeal cells combined with
bacterial cells to produce eukaryotic cells, but no general consensus has been
reached as yet. One recent model proposes that eukaryotic cells originated when
an archaeal cell engulfed bacterial cells that evolved into mitochondria, while plas-
tids originated by a later engulfment of cyanobacteria by these eukaryotic cells
(Fig. 4.11). There is no experimental evidence as yet to show that such a process
of engulfment can occur today.
Fig. 4.11
The fossil record suggests that prokaryotic cells existed at least 3500 million
years ago, but that eukaryotic fossils did not appear until around 2000 million years
later. This long gap has prompted some biologists to suggest that the origin of
eukaryotic cells is a highly improbable event, and thus if life does exist on plan-
ets outside the Solar System, it is likely to be only prokaryotic in nature. It would be
disappointing if the Earth is the only abode of eukaryotic life in the entire Universe,
since intelligent animals like ourselves are eukaryotes. On the other hand, if this
view is correct, at least we do not have to worry about invasion by advanced aliens!
The discovery of lateral gene transfer is changing the way that we think that
organisms are related to one another. We can no longer assume that all the genetic