Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
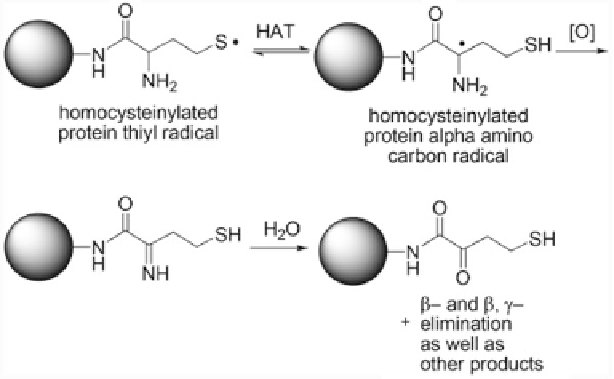
Reaction 5.2 Kinetically favored intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) process involv-
ing N-Hcy-protein promotes carbonyl formation and multiple fragmentation products including
NH
3
,H
2
S, ethylene, and
-unsaturated amides, analogous to the chemistry of free Hcy.
Captodative stabilization of the thiyl radical renders the alpha C-H bond weaker than the S-H
bond by ca. 4 Kcal/mol (Reprinted from [311])
α
,
β
The incorporation of Hcy into protein in the N-homocysteinylation reaction
results in substitution of the
-amino group of a protein lysine residue with an
Hcy residue containing a free thiol group. This leads to a decrease of the net
positive charge on a protein, due to the fact that a highly basic
ε
ε
-amino group of
a protein lysine residue (pK
a
¼
-amino group of
N-linked Hcy (estimated pK
a
~ 7). Furthermore, the introduced free thiol is sus-
ceptible to redox reactions, which generate disulfide bonds [298] or oxidative
damage [96].
Oxidative damage induced by N-homocysteinylation has been originally
demonstrated for human serum albumin [96] and hemoglobin [68]. Subsequent
studies have shown that protein oxidation occurs via kinetically favored intramo-
lecular hydrogen atom transfer from
10.5) is replaced by a less basic
α
α
-carbon to a thiyl radical (Reaction
5.2
)
[311]. The
-carbon-centered radical is detected using methyl viologen as a
probe, which turns blue in the presence of N-Hcy-albumin due to the appearance
of viologen radical. Another probe, fluorone black, affords an increase in the A
512
absorbance signal in the presence of N-Hcy-albumin, which indicates the presence
of
α
-carbon radicals react with oxygen to form
superoxide and protein carbonyls (Reaction
5.2
). The formation of protein
carbonyls in N-Hcy-albumin is detected with a colorimetric reaction with 2,4-
dinitrophenyl hydrazine, which shows a 60 % increase in the carbonyl content of
N-Hcy-albumin (containing 7-8 mol N-linked Hcy/mol protein; prepared in vitro
by incubation of human serum albumin with Hcy-thiolactone) compared with
unmodified native albumin [311].
α
-carbon radicals [311]. The
α
Search WWH ::

Custom Search