Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
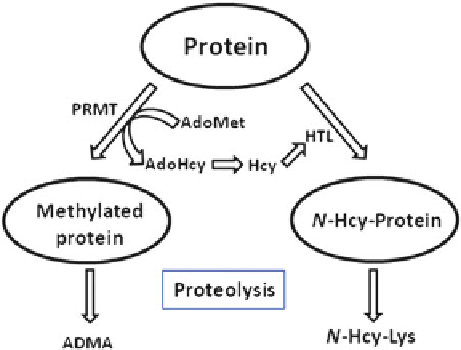
Fig. 5.5 N-Hcy-Lys and asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) are derived from the proteolysis
of modified proteins. Arginine residues in proteins are methylated by protein arginine
methyltransferase (PRMT), which uses S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) as a methyl donor and
produces S-adenosylhomocysteine (AdoHcy). Hcy derived from the enzymatic hydrolysis of
AdoHcy is converted by methionyl-tRNA synthetase to Hcy-thiolactone (HTL), which modifies
protein lysine residues, affording N-Hcy-protein. Subsequent proteolytic degradation of N-Hcy-
protein affords the isopeptide N-Hcy-Lys (Reprinted from [86])
has been utilized to synthesize Nε
-Hcy-Lys isopeptide on a preparative scale [72].
D
,
L
-Hcy-thiolactone hydrochloride (5 mmol) is incubated with
L
-lysine (5 mmol) in
100 mL 0.2 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, 0.2 mM EDTA (24 h, room
temperature). The rate of Nε
-Hcy-Lys formation increases about twofold when pH
increases from 6.0 to 7.4 and does not significantly change between pH 7.4 and 9.0.
The yield increases 1.7-fold and 1.4-fold at pH 8.0 and 09.0, respectively, relative
to the yield at pH 6.0. The reaction product, Nε
-Hcy-Lys, is purified by preparative
HPLC using a reversed-phase X Bridge Prep C18 column (19
m,
from Waters). Fractions containing Nε-Hcy-Lys isopeptide, a predominant product
eluting at 2 min, are collected dried out under vacuum to afford a white powder. The
isopeptide structure is confirmed by
100 mm, 5
μ
1
H NMR (300 MHz, D
2
O):
δ ¼
4.10 (t,
J ¼
6.6 Hz, 1H, CHNH
2
), 4.04 (t, J ¼
6.6 Hz, 1H, CHNH
2
), 3.32-3.17 (m, 2H,
CH
2
NHC(O)), 2.61 (dt, J ¼
2.4 Hz, 2H, CH
2
SH), 2.24-2.11 (m, 2H,
CH
2
CH
2
SH), 2.03-1.85 (m, 2H, HOOCCH(NH
2
)CH
2
), 1.64-1.55 (m, 3H,
CH
2
CH
2
NHC(O)), SH), and 1.51-1.36 (m, 2H, CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
NHC(O)) (chemical
shifts
7.2 Hz, J ¼
δ
in ppm, coupling constants J in Hz) [72].
-Hcy-Lys (3) has also been synthesized in a solution phase using common
procedures for peptide synthesis (Reaction
5.1
) starting from commercially avail-
able lysine derivative (
Nε
-N-Cbz-Lys-O-
0
Bu) (6) [311]. The
-NH- group in 6 is
protected by introducing the Boc-protecting group (7). The carbobenzoxy group
from the
ε
α
ε
-NH is selectively removed by catalytic hydrogenation using 10 % Pd/C
to obtain
-N-Boc-Lys-OtBu (8). The fully protected isopeptide 10 is synthesized
via amide bond formation between the free
α
ε
-NH- of 8 and the activated
Search WWH ::

Custom Search