Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
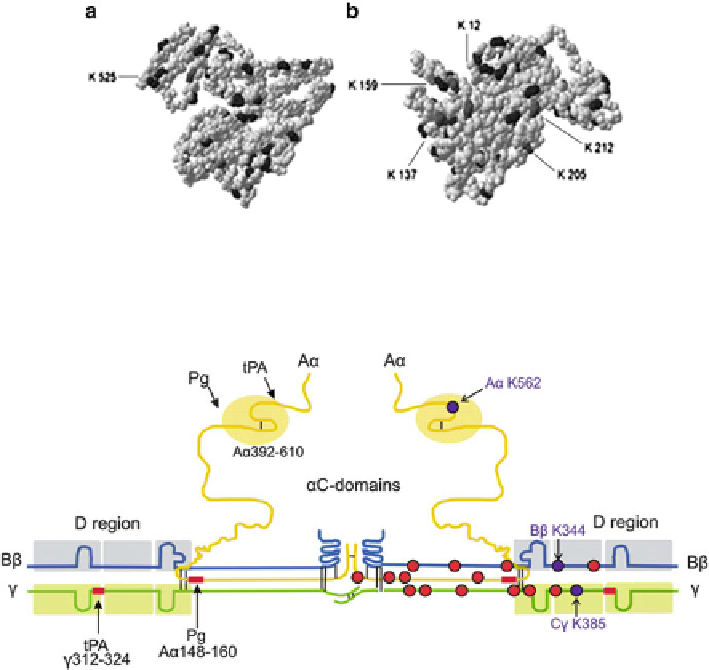
Fig. 5.2 A model of the crystallographic structure of human serum albumin based on 1 bm0.pdb.
Lysine and N-Hcy-lysine residues are highlighted with black and dark gray color, respectively. (a)
Front view. (b) A Back view. This pdb structure is missing Lys4. Lys residues 525, 205, and
137 are found to be N-homocysteinylated in vivo (Reproduced from [212])
Fig. 5.3 Schematic representation of polypeptide chain composition and independently folded
domains (boxed) in fibrinogen. Lysine residues N-homocysteinylated in vivo and in vitro are
indicated by dark-blue circles, while residues susceptible to N-homocysteinylation in vitro are
indicated by red circles [215]
In rat hippocampal neuronal cells cultured in folate-deficient media, motor
proteins kinesin and dynein become N-homocysteinylated, which leads to protein
aggregation and reduced interactions with tubulin [299]. Similar changes occur
when neuronal cells are treated with Hcy-thiolactone, suggesting that kinesin and
dynein N-homocysteinylation cause protein aggregation and prevent their physio-
logical interactions with tubulin. LC-MS analyses identify Lys1218 in the micro-
tubule-binding domain of dynein as being N-homocysteinylated, which could
account for the diminished interaction with tubulin [299].
These findings strongly support a conclusion that N-Hcy-proteins are formed in
mammalian organisms as a result of posttranslational modification of proteins by
Hcy-thiolactone.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search