Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Specificity subsite
Specificity subsite
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
S
S
S
+ATP
+tRNA
Thiol
subsite
NH
2
NH
2
NH
2
Thiol
subsite
C
C
C
O
O
O
tRNA
HO
AMP
Specificity subsite
Specificity subsite
H
S
-AMP
NH
2
SC
O
Thiol
subsite
NH
2
Thiol
subsite
NH
2
HS
C
C
O
O
AMP
AMP
Specificity subsite
Specificity subsite
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
S
S
S
R
+R-CH
2
SH
-tRNA
Thiol
subsite
Thiol
subsite
NH
2
NH
2
R
NH
2
HS
S
C
C
C
O
O
O
tRNA
tRNA
Specificity subsite
Specificity subsite
NO
NO
NO
S
S
S
+ATP
+tRNA
Thiol
subsite
NH
2
NH
2
NH
2
Thiol
subsite
C
C
C
O
O
O
AMP
tRNA
HO
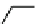
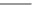
Fig. 3.8 Reactions catalyzed by MetRS. From top to bottom: the aminoacylation of tRNA with
Met, the synthesis of Hcy-thiolactone during Hcy editing, the synthesis of methionyl thioesters, the
aminoacylation of tRNA with S-NO-Hcy (Reproduced from [76])
including human [241]. Similarly, Asp52, which is responsible for the recognition
of the amino nitrogen of the methionine substrate, is also conserved in the protein
sequence of all species. Along with these, Tyr260 is also conserved in the primary
structure of all species. The variations in the MetRS active site residues among
different species are shown in Table
3.7
.

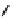

















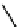
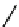
























































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search