Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
25
Hcy
2
Hcy-thiolactone
80
20
60
1
15
urine
+
NaOH
1
40
3
10
2
3
20
ur
ine
1
3
3
0
5
1
STD
-20
4
0
0
2
4
6
8
10
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
Minutes
Minutes
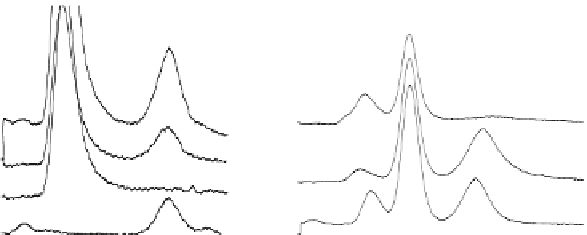
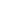
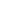
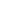
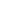
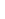
Fig. 3.4 Determination of Hcy-thiolactone by cation exchange HPLC. Detection is by fluores-
cence emission at 480 nm (excitation at 370 nm) after post-column derivatization with OPA. Left
panel: plasma Hcy-thiolactone. Analyses of samples prepared from human plasma containing 6.7
and 2.8 nM Hcy-thiolactone are illustrated by trace 1 and trace 2, respectively. Hcy-thiolactone is
absent in plasma samples treated with NaOH before HPLC analysis (trace 3). Hcy-thiolactone
standard (100 fmol) elutes at 8 min (trace 4). A peak eluting in a void volume is due to Hcy present
in plasma samples. Right panel: urinary Hcy-thiolactone. Samples prepared from human urine
(containing 538 nM Hcy-thiolactone) before (middle trace) and after 5-min treatment with 0.1 M
NaOH (top trace). Lower trace (labeled STD) was obtained with a standard sample containing
0.5 pmol Hcy (peak 1), 200 pmol histidine (peak 2), 1 pmol Hcy-thiolactone (peak 3) (Reproduced
from [94, 95])
The first universal HPLC assay that allows analysis of Hcy-thiolactone in any
biological samples, including human and mouse plasma [94], urine [95], and tissues
[140, 141], has been developed by using a cation exchange PSEA column, post-
column derivatization with OPA, and fluorescence detection (excitation at 370 nm,
emission at 480 nm). The plasma Hcy-thiolactone assay involves ultrafiltration on
Millipore 10-kDa cutoff device to remove protein followed by selective extraction
of Hcy-thiolactone from the deproteinized sample. A crucial step in sample prepa-
ration is chloroform/methanol extraction, which is more selective than the charcoal
extraction [64] for plasma samples. Further purification and quantification are
achieved by HPLC on a cation exchange PSEA column and fluorescence detection
after post-column derivatization with OPA/NaOH. The limit of detection is
0.36 nM. As little as 25 fmol Hcy-thiolactone in a sample can be detected and
quantified [94, 95]. Examples of HPLC analyses of human plasma and urinary Hcy-
thiolactone are shown in Fig.
3.4
. Using this assay, Hcy-thiolactone concentrations
in plasma from normal healthy human subjects (n ¼
60) were found to vary from
6.13 nM. In 29 of the 60 human plasma
samples analyzed, Hcy-thiolactone levels were below the detection limit. This
method has also been successfully used in the first studies of human urinary Hcy-
thiolactone excretion, which found that the bulk of Hcy-thiolactone formed in the
human body is cleared by the kidney [95]. Charcoal extraction is a crucial step
in the determination of urinary Hcy-thiolactone. Hcy-thiolactone concentrations
in human urine (11-485 nM; n ¼
0.1 to 34.8 nM, with an average of 2.82
<
19) are 100-fold higher than in plasma




















































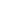


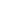

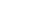





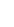
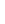
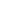
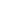
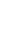

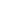





















Search WWH ::

Custom Search