Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
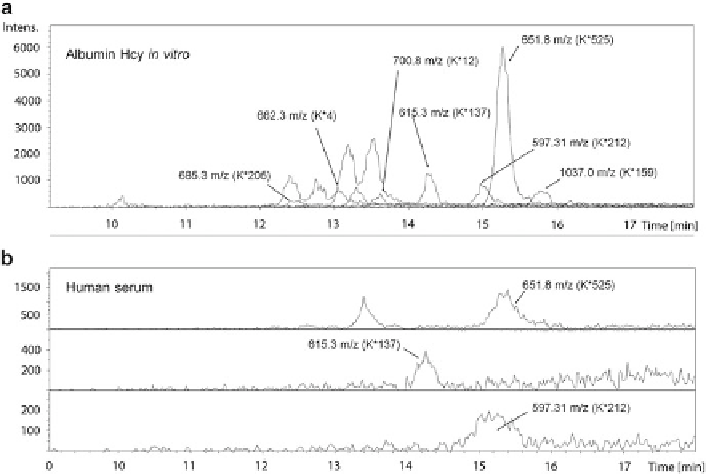
Fig. 5.15 Mass spectrometric identification of N-Hcy-Lys residues in N-homocysteinylated
albumin. LC-ESI-MS chromatograms of selected ions of N-Hcy-Lys-peptides obtained by the
digestion with trypsin of in vitro N-homocysteinylated human serum albumin (panel a) and
N-Hcy-Lys-peptides of albumin from tryptic digests of human serum from a CBS-deficient
hyperhomocysteinemic subject (panel b) (Reproduced from [212])
(
1
DAHK*SEVAHR
10
, 1,323.6 m/z), K12 (
11
FK*DLGEENFK
20
, 1,400.7 m/z), K137
(
137
K*YLYEIAR
144
, 1,229.7 m/z), K159 (
146
HPYFYAPELLFFA K*R
160
, 2,073.1 m/z),
K205 (
200
CASLQK*FGER
209
1,369.6 m/z), and K212 (
210
AFK*AWAVAR
218
,
1,193.6 m/z), in addition to previously identified K525 (
525
K*QTALVELVK
534
,
1,302.8 m/z) [96] in human serum albumin, are susceptible to the modification by
Hcy-thiolactone in vitro.
The identity of N-homocysteinylation sites in human serum albumin is
confirmed by additional tandem mass spectrometric analyses using LC/ESI-MS/
MS system consisting of nano-LC chromatograph hyphenated to q-ToF hybrid
mass spectrometer. Identification of the seven N-Hcy-Lys-peptides in tryptic digest
of N-Hcy-albumin is achieved in a single analysis in this system (Fig.
5.15
). From
the recorded mass spectra, it is possible to deduce sequences of all seven consecu-
tively eluted N-Hcy-Lys-peptides. Retention times of peptides together with CID
MS/MS spectra for the four most abundant N-Hcy-Lys-peptides unequivocally
confirmed their structures [212].
Knowing the masses of Hcy-containing peptides derived from the in vitro-
prepared N-Hcy-albumin, we can determine whether these peptides are present in
samples prepared from native human serum. For this purpose, human serum is
diluted 60-fold with 50 mM NH
4
HCO
3
and reduced with 1 mM DTT at 95
C for
5 min. Thiol groups are blocked with 4 mM iodoacetamide at 22
C in the dark for
20 min, and the serum protein is digested with sequencing grade trypsin. Tryptic
Search WWH ::

Custom Search