Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
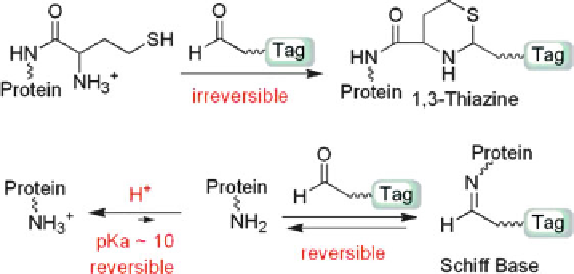
Reaction 5.6 In reactions of aldehydes with N-Hcy-protein, 1,3-thiazine formation is favored
over Schiff base formation under acidic conditions (Reprinted from [214])
N-Hcy-myoglobin-rhodamine aldehyde adduct (excitation at 450 nm, emission at
520 nm) after separation on SDS-PAGE gels shows that the assay is linear from
160 ng to 2.5
g modified myoglobin. The detection limit is 80 ng N-Hcy-myoglo-
bin [214], corresponding to 1.8 pmol N-linked Hcy in myoglobin.
The rhodamine aldehyde tagging assay detects protein N-homocysteinylation in
biological samples. For example, normal human serum, which is known to contain
small amounts of N-Hcy-albumin [96], is labeled with rhodamine aldehyde and N-
Hcy-myoglobin is added as a standard. After separation on SDS-PAGE gels, the
fluorescence signal is detected in the albumin band, in addition to the band of N-
Hcy-myoglobin used as a positive control [214].
Using this approach but with a different tag, biotinylated aldehyde, increases
the sensitivity and allows detection of N-linked Hcy in human and rat proteins
[214]. After incubation with biotinylated aldehyde (pH 3.0, 25
C, 8 h), proteins
are separated by SDS-PAGE, subjected to Western blotting, and detected by
chemiluminescence using streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase, SuperSignal West
Pico chemiluminescence substrate, and FluoroChem Imager SP. In this assay, the
extent of N-homocysteinylation is found to be greater in rat hemoglobin than that
observed in human hemoglobin. The biotin aldehyde labeling assay also
demonstrates higher levels of N-homocysteinylation in rat serum proteins, com-
pared with human serum proteins [214]. These results are consistent with
previous assays of N-linked Hcy in hemoglobin and albumin from different
species (Table
5.7
) using an HPLC-based method [297] and provide a validation
for the biotin aldehyde labeling approach.
Selective reactions with aldehydes can also be used for affinity enrichment of N-
Hcy-proteins or N-Hcy-peptides, usually present at low abundance, to increase
sensitivity of their detection [214]. For this purpose aldehyde resins are used.
Tryptic peptides obtained from N-Hcy-proteins are passed through the Self Pack
POROS 20 AL resin functionalized with an aliphatic aldehyde. After washing
unbound peptides, the bound N-Hcy-peptides are eluted by three treatments with
O-methylhydroxylamine. The combined eluted fractions are concentrated and
μ
Search WWH ::

Custom Search