Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 14.10
Countermeasures against HFS
In this study, we clarified the HFS process using the expectancy theory of
motivation and information prospectability. Further empirical research based on
other case studies is required.
Finally, there are two implications arising from this study. One concerns encour-
aging users of social media to offer information. There are several approaches that
can be used to encourage users. One involves offering rewards that have positive
valences to users and increasing the instrumentality of rewards. In HFSs, galleryites'
posts serve this function. Unlike HFS, in which information-offering is done by
anonymous users in most cases, if users offering information contributed with
specific ID, it would mean that previous records of contributions they had made
could be shown and it can be some kind of rewards. Another approach to encouraging
information-offering is decreasing the required cost for the information behavior.
Although most of the cost depends on users' attributes, the cost for discerning desired
information could be decreased by organizing information which is typically done by
On-A contributors in HFS.
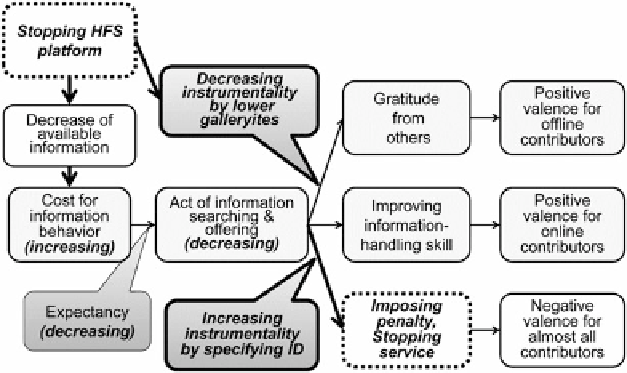
This study also indicates countermeasures against HFSs invading someone's
privacy. These are also based on manipulation of the costs of information behavior,
valence, and instrumentality (Fig.
14.10
). Stopping the HFS platform brings about
increases in information-discerning costs thorough being unable to use a place
where information about the target of HFS is accumulated. Because stopping the
HFS platform means stopping the 'theater' where many galleryites concentrate, it
brings about decreases in positive valence and instrumentality. It is also effective to
increase negative valences by imposing penalties for contributors. The develop-
ment of laws against invading privacy would make negative valences and
instrumentalities clear. Also regulation by a platform provider, based on terms of
use, can be effective. Stopping the service for users involved in HFSs acts as a
negative valence. Additionally, specifying users' IDs brings about an increase in
instrumentality whether its valences are positive or negative.