Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
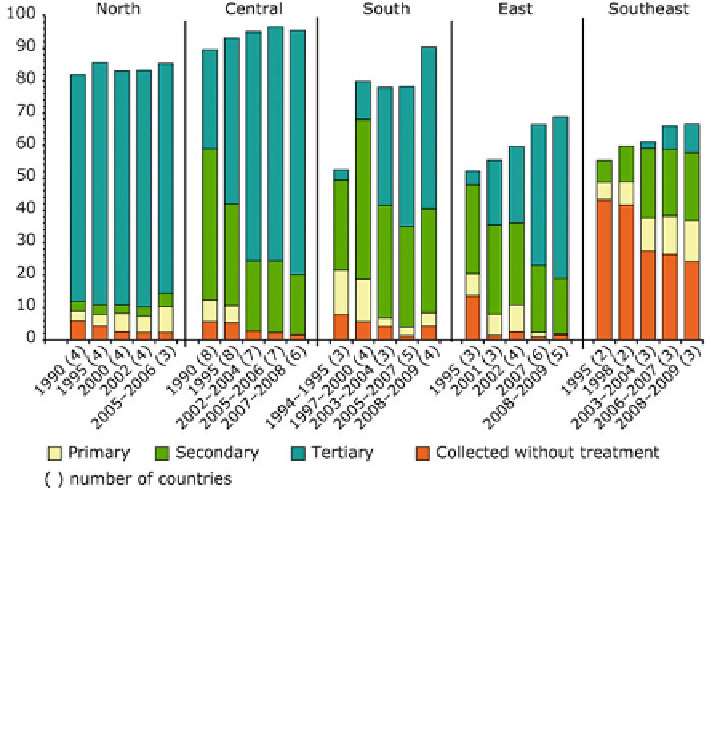
Fig. 1 Population connected to waste water collection and UWWTPs (Urban Waste Water
Treatment Plants).
Source
EEA (
2013
).
Notes
Primary (mechanical) treatment removes part of the
suspended solids. Secondary (biological) treatment uses aerobic or anaerobic microorganisms to
decompose most of the organic matter and retain some of the nutrients (around 20
-
30 %). Tertiary
(advanced) treatment removes the organic matter even more efficiently and generally includes
phosphorus retention and in some cases nitrogen removal.
North
Norway, Sweden, Finland and
Iceland.
Central
Austria, Denmark, England and Wales, Scotland, the Netherlands, Germany,
Switzerland, Luxembourg and Ireland.
South
Cyprus, Greece, France, Malta, Spain and Portugal.
East
Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Slovenia, Slovakia.
Southeast
Bulgaria, Romania and Turkey
Belgium), the ecological status of water is not good (EEA
2012
, p. 12) due to
intensive agriculture. Nevertheless, the EEA acknowledges in its Environmental
Indicator Report 2013 that some pollutant emissions have been reduced signifi-
-
cantly in the past 25 years. Furthermore,
cant
improvement of the chemical quality of water within the last three decades; how-
ever,
the agency observes a signi
(EEA
2013
, p. 67). The European WFD is intended to interfere at this point aimed at
reaching a good ecological and chemical quality of waters until the year 2015 (EP
and EC
2000
). In this context, there is a particular need for action for the original
polluters (e.g. agriculture), while the impact of water and wastewater management
on the water quality is principally positive.
“…
10 % of Europe
'
s surface waters
…
have poor chemical status
”
Search WWH ::

Custom Search