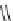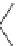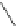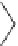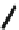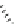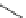Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 18
Structure of
macrocyclic amide (
M
,
M
)-
74
[
63
]
HN
NH
O
O
O
O
HN
NH
(
M
,
M
)-
74
H
H
H
H
N
NHBoc
BocHN
N
N
N
O
O
O
O
R
R
R
n-1
75
:R =CO
2
n
-C
10
H
21
Fig. 19
Structures of amidohelicene oligomers
75
[
67
]
chloroform and benzene at concentrations above 2 mM. The diastereomeric
(
M
,
P
,
M
)-
76
forms aggregated dimer only above 15 mM. Effects of substituents
and structures of linking groups on intra- and intermolecular aggregation by
p
-
p
interactions have also been investigated [
68
-
70
].
A series of optically active acyclic alkyne oligomers
77
(Fig.
21
) containing two
to nine units of (
P
)-
71
and bearing decyloxycarbonyl side chains have been
synthesized [
71
]. In chloroform, heptamer (
n ¼
7), octamer (
n ¼
8), and nonamer
(
n ¼
9) form helical and dimeric structures, most likely double helices, whereas the
lower oligomers form random-coil structures. Heptamer gradually unfolds to a
random-coil structure in chloroform at room temperature.
CD and VPO studies reveal that acyclic alkyne pentamer (
P
)-
78
(Fig.
22
)
bearing perfluorooctyl side chains forms a homo-double-helix structure in trifluor-
omethylbenzene, a strong helix-forming solvent [
72
]. Unlike in chloroform,
pentamer (
P
)-
77
(
n ¼
5) also forms a homo-double-helix structure in trifluoro-
methylbenzene. Interestingly, the mixture of (
P
)-pentamer
78
and (
M
)-pentamer of
77
(
n ¼
5) produces a hetero-double-helix dimer, indicating its higher stability over
the homo-double-helix dimers of (
P
)-
78
and (
M
)-
77
(
n ¼
5). On the other hand, the