Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
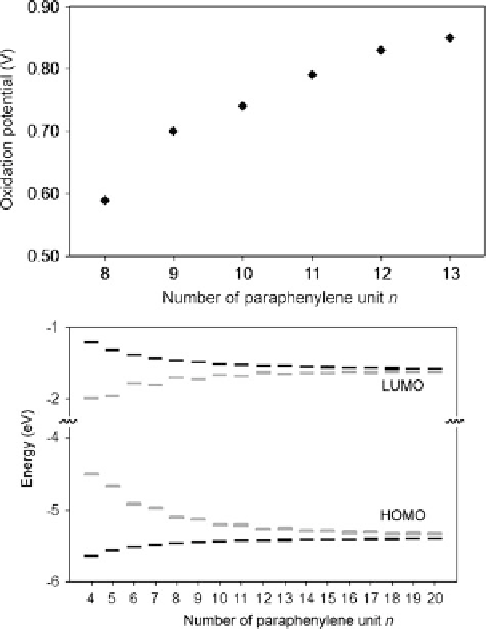
Fig. 31
Top
: observed oxidation potential of [
n
]CPP.
Bottom
: calculated HOMO-LUMO gaps for
[
n
]CPP (
gray
) and [
n
]OPP (
black
)[
38
]
terphenyl in the resulting macrocycle explains the relatively low macrocyclization
yield. Even so, this molecule was easily aromatized using sodium naphthalenide at
78
C, yielding 1.0 mg of [7]CPP. The final step of any CPP synthesis must
necessarily introduce a large amount of strain. These results highlight the reductive
aromatization methodology as quite capable of generating large amounts of strain
energy at low temperatures. Interestingly, [7]CPP displays an orange fluorescence,
further red-shifted than [8]CPP and with a very low quantum yield, following the
trends observed in larger carbon nanohoops [
43
].
A revision of the [7]CPP synthesis to incorporate more curvature in the precursors
would allow for the construction of even smaller CPPs, approaching the theoretical
limit of the benzenoid structure [
64
]. With this in mind, Jasti developed a sequential
lithium addition/oxidative dearomatization strategy by which tightly-curved
dibromide 70 can be obtained on a multigram scale (Fig.
33
)[
49
].
The addition of lithiated 4-bromo, 4
0
-
tert
-butyldimethylsilyl biphenyl to 63
followed by methylation and deprotection offered 68 which could be subjected to