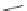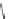Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Br
OMOM
(HO)
2
B
B(OH)
2
n
X
OMOM
Pd(PPh
3
)
4,
NaCO
3,
n
Bu
4
Br
THF/H
2
O, 60˚C
Br
MOMO
OMOM
57a
: X = Br, n = 1, 59%
57b
: X = Br, n = 2, 76%
56
Pd
2
(dba)
3
, X-Phos
B
2
pin
2
, KOAc
1,4-dioxane/H
2
O, 90˚C
58a
: X = Bpin, n = 1, 87%
58b
: X = Bpin, n = 2, 81%
n
57
+
58
OMOM
X
OMOM
Pd(OAc)
2
, X-Phos, NaOH
1,4-dioxane/H
2
O, 80˚C
MOMO
OMOM
MOMO
OMOM
NaHSO
4
·H
2
O
m
-xylene/DMSO
reflux under air
59a
: 45% from
57a
+
58a
59b
: 32% from
57b
+
58a
59c
: 43% from
57b
+
58b
[14]CPP: 37%
[15]CPP: 43%
[16]CPP: 28%
x
y
MOMO
OMOM
MOMO
OMOM
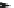
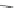
Fig. 26 Itami's synthesis of [14]CPP, [15]CPP, and [16]CPP [
36
]
4.4 Better Synthetic Control and New CPP Sizes
With three unique synthetic strategies, each lab pushed forward to create new sizes
of cycloparaphenylene and to do so selectively. In 2010, Itami reported a modified
synthesis that offered access to [14]CPP, [15]CPP, and [16]CPP selectively via
U-shaped dibromide precursors with seven or eight rings (Fig.
26
)[
36
]. These new
intermediates 57a and 57b were the products of palladium coupling of a molar
excess of 56 with 1,4-phenylboronic acid or 4,4
0
-biphenylboronic acid.
Either of these dibromides can then be converted to the corresponding
bisboronates 58a and 58b by palladium-mediated borylation and Suzuki coupled