Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
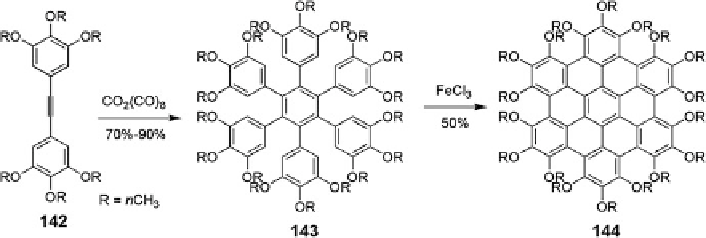
Scheme 17 Synthesis of non-planar peralkoxylated HBC [
106
]
Based on a novel synthetic concept, plenty of HBC derivatives with different
substituents in the peripheries were synthesized to serve different purposes. Among
them, most of the HBC derivatives are deemed planar due to the planarity of the
aromatic core. In contrast, an interesting example is the peralkoxylated HBC 144
which adopted nonplanar aromatic backbones due to the steric congestions between
the substituents at the bay regions. The synthetic route involved Co
2
(CO)
8
-assisted
cyclotrimerization and the subsequent oxidative cyclization of 143 with FeCl
3
(Scheme
17
). Single-crystal analysis revealed that the outer phenyl rings flip up
and down in an alternating manner with respect to the inner core and a significant
deviation from planarity with a maximum angle of 16.8
o
, which resulted in a
“double-concave” conformation. This nonplanar HBC represented a good supra-
molecular host for nonplanar fullerene and electron-deficient perfluorobenzene,
which was proven by the analysis of cocrystals of compound 144 and fullerene
C
60
, indicating that C
60
was perfectly included by the complementary double-
concave geometry with a 1D columnar structure [
106
].
Very recently a novel HBC derivative 151 with
C
3
-symmetry was developed
(Scheme
18
)[
107
]. In this synthetic sequence, the HBC core 150 was first
constructed, where the methylene chloride functional groups in 150 provided the
possibility to convert into triphosphate derivative 151, which allowed the synthesis of
the so-called octupolar HBC chromophores with “push-pull” motif by threefold
Wittig-Horner reactions between triphosphate derivative and corresponding benzal-
dehyde derivatives. Notably, these chromophores exhibited large TPA cross-sections
up to 16,718 GM (at 760 nm), which are among the best of TPA chromophores. The
TPA properties were found to depend on the electron-acceptor strength, the solvent
polarity, and the concentration. These chromophores added a new design concept of
using large PAHs as potential TPA chromophores in the future.
As mentioned above, the HBC derivatives substituted with alkyl chains can form
self-assembled 1D columnar structures due to strong
interactions between the
rigid aromatic core and the nanoscale phase separation between the rigid core and
the flexible alkyl chains at the periphery, which facilitates the overlap of
p
-
p
p
-orbitals
between neighboring planes and maximizes the charge transport ability along the
1D columns. Therefore the control of supramolecular order of HBC derivatives