Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
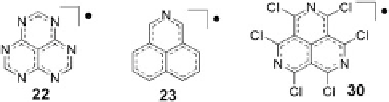
Fig. 8 Other nitrogen-containing phenalenyl radicals [
23
-
25
]
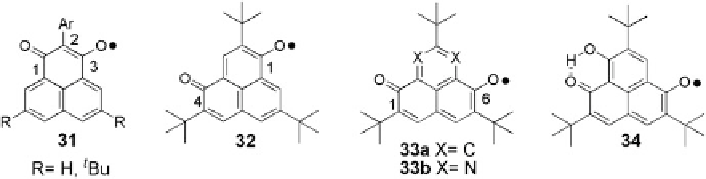
Fig. 9 Oxophenalenoxyl radicals [
27
-
34
]
So far, several types of oxophenalenoxyl systems have been prepared (Fig.
9
).
Among them, the 3-oxophenalenoxyl 31, having two oxygen atoms at 1,3-positions
of the phenalenyl skeleton, appeared to be quite unstable and oxidation of the
corresponding hydroxyl precursors generally led to closed-shell
s
-dimers. Pyroly-
sis of the
-dimer gave the neutral radical in solution, although this radical could
not be isolated [
27
-
30
]. The trend of formation of such a
s
-dimer was explained by
the large spin density distribution at the 2-position and oxygen atoms. In sharp
contrast, the 4- and 6-oxophenalenoxyl derivatives 32 and 33a with oxygen atoms
at the 1,4- and 1,6-positions are expected to perform higher thermodynamic stabil-
ity due to the extensive spin delocalization [
31
]. Introduction of
tert
-butyl groups as
steric protection further increases the kinetic stability of those systems which
enables them to be handled in air [
32
]. With the same strategy, the 7-hydroxy-6-
oxophenalenoxyl derivative 34 was prepared as the first neutral radical with an
intramolecular hydrogen bond [
33
]. A 7,9-diaza-6-oxophenalenoxyl derivative 33b
was designed and represented an interesting motif to construct bridging ligands for
intermolecular networks. However, this radical is extremely sensitive to sunlight
even at very low temperatures which may be due to a lowering of SOMO energy
level and decrease of the SOMO-LUMO gap [
34
].
The ability of oxophenalenoxyl radicals to form functional organic materials was
also examined by tetrathiafulvalene (TTF) molecule as an electron donor. It was
found that TTF-substituted oxophenalenoxyl radicals exhibited tunable intramolecu-
lar electron transfer (IET) by moderate change of external environments such as
solvent and temperature in solution, leading to “spin center transfer” accompanied by
solvato-/thermochromism (Fig.
10
). There were two species involved in this process,
a neutral radical 35 existing in dichloromethane solution with most of the spin
localized on oxophenalenoxyl motif, and a zwitterionic radical 36 existing in trifluor-
oethanol solution with spin localized on TTF moiety as radical cation species.
s