Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
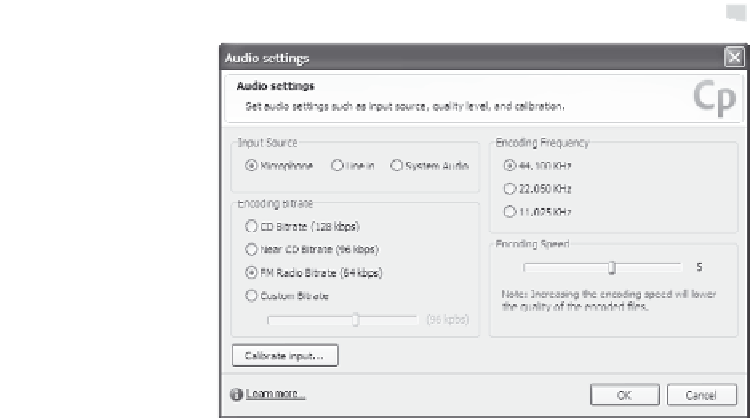
Figure 8-4. Set audio quality.
4.
Choose one of the available sources for audio input:
Microphone
Line in
System Audio
5.
Choose one of the encoding frequencies. This is the number of
times per second the original sound wave is translated into digital
form. A higher frequency results in a more accurate digital repre-
sentation of the sound.
44.100 KHz—The most frequent sampling; gives the highest
quality (near CD quality)
22.050 KHz—Comparable to FM radio
11.025 KHz—Fewer samples per second, resulting in lower
quality sound; generally considered equivalent to telephone
quality, but actually a little higher
6.
Choose one of the encoding bitrates. This specifies the amount of
audio information (in kbps) that will be stored per second of a
recording:
CD Bitrate (128 kbps)—This setting gives you the highest
quality, and largest file size.
Near CD Bitrate (96 kbps)—This setting is close to CD qual-
ity, but creates a smaller file size.