Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
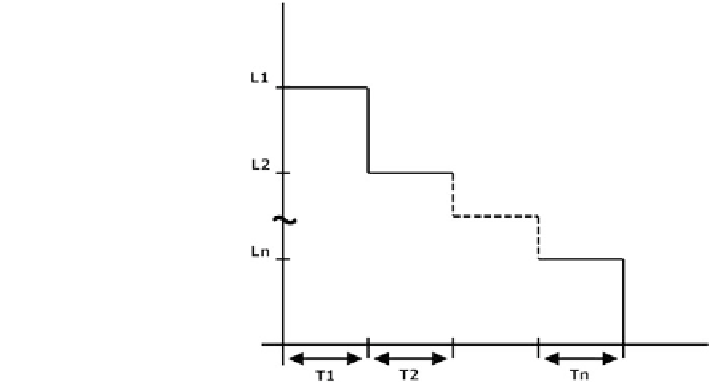
Fig. 5 Variation of load (x-
axis) with time (y-axis)
(a) Static Cost Based Planning Method
In distribution system, the shunt capacitor increases the system ef
ciency. The
objective of optimal capacitor placement is to reduce the power loss, energy
loss, and to minimize the cost of capacitor banks, while maintaining bus
voltages within prescribed limits (Kumar and Singh
2011
). Based on these
objectives in conventional method of planning, the objective function is for-
mulated as
C
j
u
j
k
e
X
nl
X
nc
u
i
u
0
min f
ð
;
Þ¼
T
i
P
i
þ
k
p
P
l
þ
ð
12
Þ
i
¼
1
j
¼
1
u
j
Þ
where, T
i
is time duration, nl is load level, C
j
ð
is cost function of capacitor
k
cj
u
j
, k
cj
is the capacitor cost, k
inst
is the capacitor installation
cost, nc is number of capacitors, Y is planning years, Pi
i
power loss at load
level i, k
e
is cost of energy, Pl is power loss at peak load, k
p
is cost of peak
power loss.
(b) Variable Cost Based Planning Method
The static cost based planning method assumes the cost to remain constant
over the planning period, which is not the case. In the variable cost based
planning method, the objective function of static cost based planning method
is reformulated to include the variation in the cost. The variation in the cost is
incorporated by inclusion of the cost of maintenance, and the variation in the
cost due to certain economic factors. These costs need to be included while
minimizing the total cost of the system for achieving the targets (Kumar et al.
2014
). The reformulated objective function can be expressed as
u
j
Þ¼
C
j
ð
k
inst
þ
Search WWH ::

Custom Search