Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
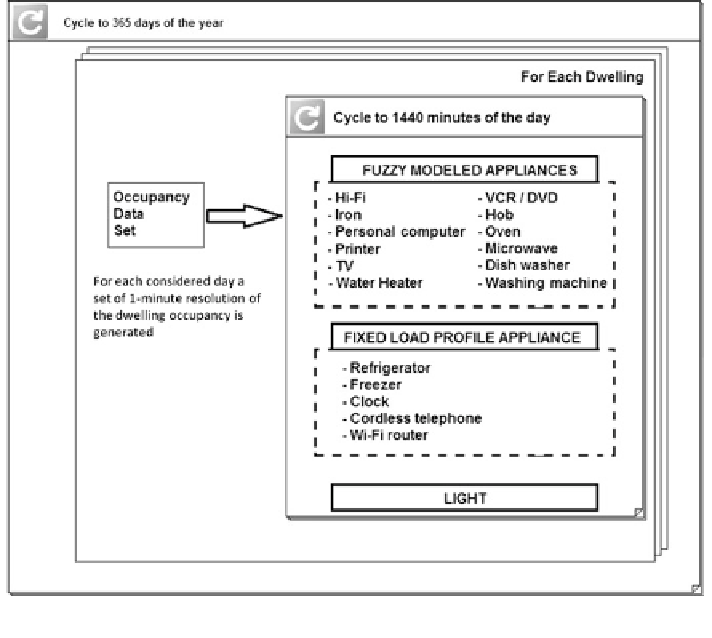
The model has been realized using LabVIEW, the graphical programming
environment of National Instruments. In particular the FIS has been realized using
the LabVIEW fuzzy toolkit while the input-output membership functions and the
rule set with the fuzzy system designer. As the simulator is not time driven when a
simulation runs one-min resolution electricity demand data can be generated for a
speci
ed time period using two nested FOR loops (the outer for the days of the year
and the inner for the minutes of each day) as shown in Fig.
5
.
Each single appliance block, implemented as a functional global variable, is in
the inner loop and runs in two phases. During the
first iteration of the simulation all
the con
guration parameters are loaded, e.g. the fuzzy rule set of the appliance, the
consumption pro
le, the maximum power, the typical starting frequency, number of
people typically interacting with the appliance (all the mentioned parameters are
fully editable in text
files and fuzzy rules through LabVIEW graphical interface).
first iteration the likelihood an appliance will start within the next
minute is evaluated with a time resolution of one-minute (except for the so called
“
After the
). In particular, since the FIS output is a probability
value, to manage the start of an appliance this value is multiplied by a calibration
Continuous use appliances
”
Fig. 5 Structure of the LabVIEW simulator
Search WWH ::

Custom Search