Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 3 Dishwasher FIS
sample
VA A IT L VL
EM VL VL VL VL VL
M VL VL VL L L
A VL VL L L M
E VL L M H VH
LE VL VL VL VL VL
Input DT/T(t) is in the
first row, while h(t) is in the
first column.
Probability P(t) are the central values of the table
A sample of the fuzzy control rule base for a
“
Periodical use appliance without
human interaction
(e.g. the dishwasher) is shown in Table
3
; the Max-Min fuzzy
inference algorithm is considered, (Bose
2011
). The outputs of the FIS engine are
the probability P(t) to start a certain appliance: (N) None, (VL) Very Low, (L) Low,
(M) Medium, (H) High, (VH) Very High and the total time D(t) the appliance will
be on: (VL) Very Low, (L) Low, (M) Medium, (H) High, (VH) Very High. Output
membership functions, shown as example in Fig.
4
, consist of sigmoid functions
with different values for each appliance category.
Concerning the defuzzyfi-
”
-
cation method since the centroid method evaluates the area under the scaled
membership functions only within the range of the output linguistic variable and the
resulting crisp output values could not span the full range. The fuzzy logic con-
troller uses the following equation to calculate the geometric center of the full area
under the scaled membership functions:
mCoA =
R
f(x)
cation we use the modi
ed Center of Area defuzzyfi-
xdx
R
f(x)dx
ð
2
Þ
where mCoA is the modi
ed center of area. The interval of integration is between
the minimum membership function value and the maximum membership function
value. Note that this interval might extend beyond the range of the output variable.
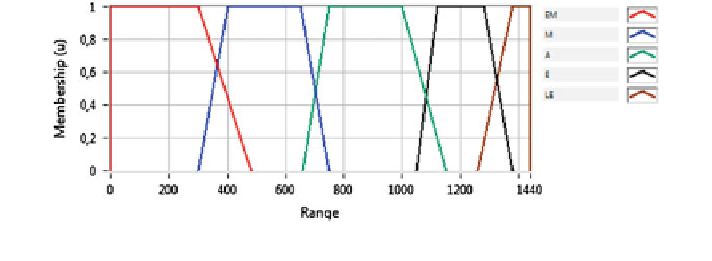
Fig. 1 Membership function of the input variable h(t). The x-axis is the time of the day in minutes






Search WWH ::

Custom Search