Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
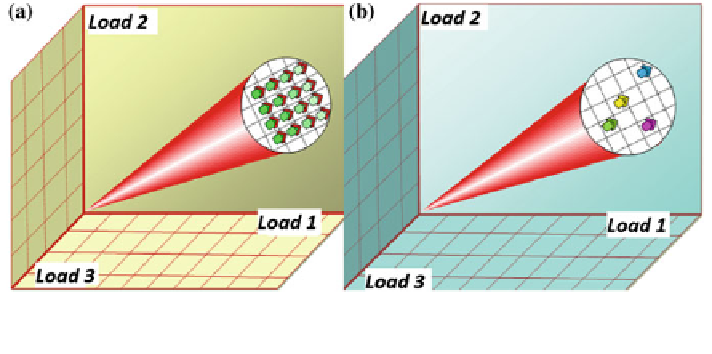
Fig. 7 Sampling homothetic stress directions for boundary identification. a Traditional stratified
sampling. b Latin hypercube sampling
4.2 Stage II
Importance Sampling
—
Once the boundary region has been identi
ed, the next step is to sample operating
conditions from that. This section describes the central concept behind embedding
such intelligence in the sampling approach.
The standard Monte Carlo sampling approach draws values for each parameter in
proportion to the assigned distribution. Given the previous knowledge of the
boundary region from Stage I, biasing the sampling process towards the boundary
region can be implemented using the importance sampling method, which helps in
maximizing the information content. In this study, the inter-load correlations are
captured in the sampling process using copulas (Papaefthymiou and Kurowicka
2009
), unlike many studies that approximate the inter-load correlations using mul-
tivariate Normal distribution for computational purposes. Copulas are generated
based on non-parametric historical load distribution, and it enables sampling realistic
scenarios.
4.2.1 Importance Sampling Variance Reduction
In risk-based security planning studies, the quantity of interest is probability of
unacceptable performance, i.e., P(Y
*
unacceptable events) (Billinton and Li
1994
).
Z
t
P
ð
Y
t
Þ¼
f
ð
y
Þ
dy
ð
3
Þ
\
1
where, y = t denotes the threshold performance such that y < t is unacceptable per-
formance. The indicator function I(y) denoting region of interest h(y)isde
ned as,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search