Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
p
p
p
p
p
(c)
(d)
p
p
p
p
p
p
p
p
p
p
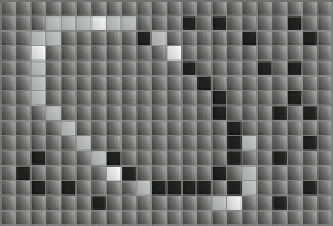
Fig. 5 Evaluation of a candidate solution E: the image in (a) shows the original edge map while
(b) presents the individual E = p
1
, p
2
, p
3
, p
4
and p
5
to be evaluated. The image (c) shows the virtual
shape S and its corresponding pixels in bold line. The image in (d) shows coincidences between
both images which have been marked by darker pixels while the virtual shape is also depicted
through a dashed line
presents the generated virtual shape drawn from points p
1
, p
2
, p
3
, p
4
and p
5
. Finally,
Fig.
5
d shows the virtual shape S compared to the original image, point by point, in
order to
find coincidences between virtual and edge points.
The virtual shape S (Fig.
5
c), obtained by MEA, gathers 47 points (N
s
= 47) with
only 25 of them existing in both images (shown as darker points in Fig.
5
d) and
yielding:
P
Ns
25, therefore J(E) = 0.255. This value indicates that the
virtual shape S obtained, has a considerable number of coincidences with the edge
map.
v
¼
1
G
ð
x
v
;
y
v
Þ¼
3.4 Implementation of DE for Ellipse Detection
The ellipse detector algorithm based on DE can be summarized in the following
steps:




Search WWH ::

Custom Search