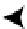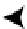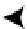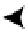Database Reference
In-Depth Information
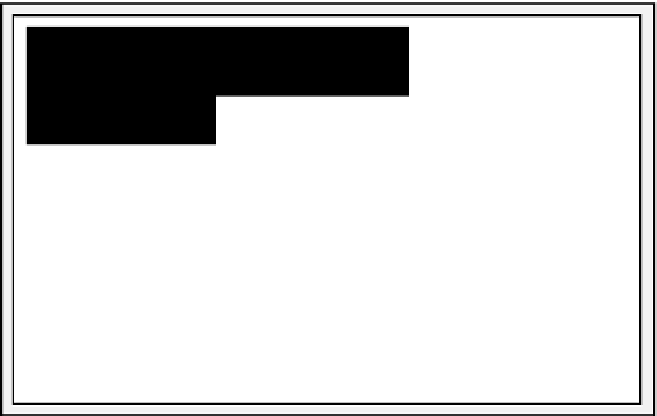
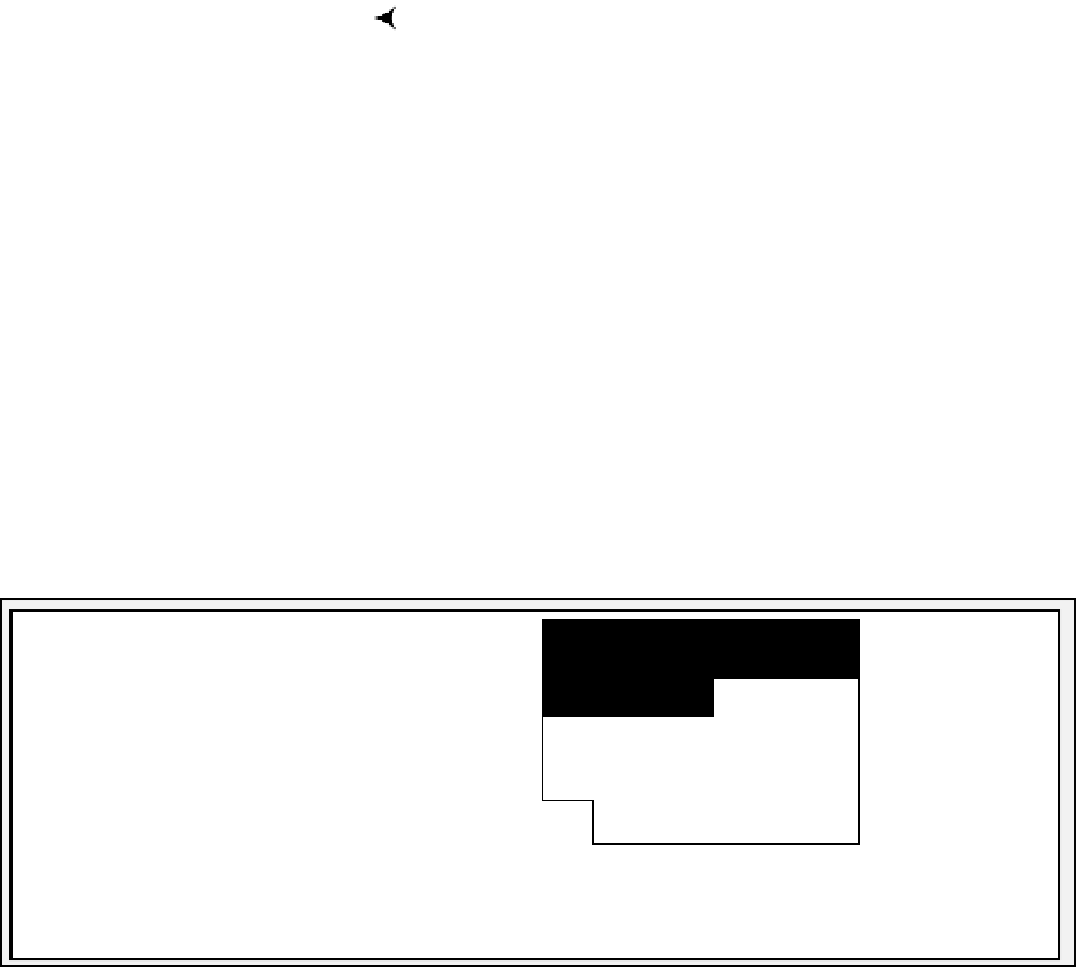
Block Header
Free Space
Row 4 Data
Row 3 Data
Row 2 Data
Row 1 Data
Figure 10-4.
Data block as it would appear after coalescing free space
If the row fit into the coalesced space, it would have happened. This time, however, Oracle will not perform
this coalescing and the block will remain as it is. Since row 4 would have to span more than one block if it stayed on
this block, Oracle will move, or migrate, the row. However, Oracle cannot just move the row; it must leave behind a
forwarding address. There may be indexes that physically point to this address for row 4. A simple update will not
modify the indexes as well.
■
there is a special case with partitioned tables that a rowid, the address of a row, will change. We will look
at this case in Chapter 13. additionally, other administrative operations such as
FLASHBACK TABLE
and
ALTER TABLE
SHRINK
may change rowids assigned to rows as well.
Note
Therefore, when Oracle migrates the row, it will leave behind a pointer to where the row really is. After the
update, the blocks might look as shown in Figure
10-5
.
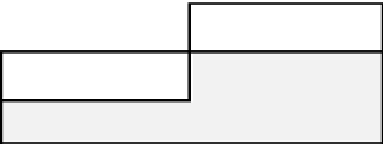
Block Header
Block Header
Free Space
Free Space
Row 4 Data
Row 3 Data
Row 2 Data
Free Space
Row 1 Data
Row 4 Migrated
Data
Figure 10-5.
Migrated row depiction