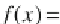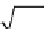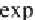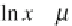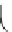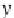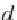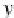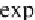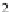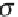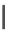Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Logarithmic Normal or Log-Normal Distribution
h e
logarithmic normal
or
log-normal distribution
is used when the data have
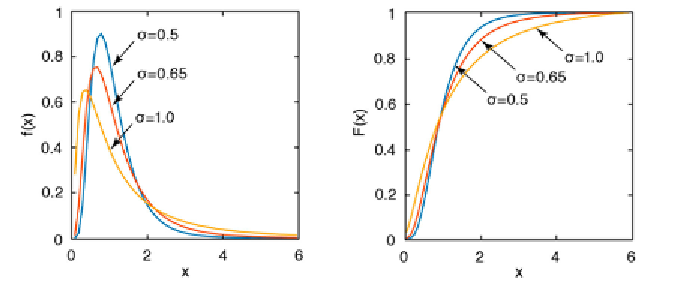
a lower limit, e.g., mean-annual precipitation or the frequency of earthquakes
(Fig. 3.8). In such cases, distributions are usually characterized by signii cant
skewness, which is best described by a logarithmic normal distribution. h e
probability density function of this distribution is
and the cumulative distribution function is
where
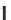
x
>0. h e distribution can be described by two parameters: the mean
ʼ and the standard deviation ˃. h e formulas for the mean and the standard
deviation, however, are dif erent from the ones used for normal distributions.
In practice, the values of
x
are logarithmized, the mean and the standard
deviation are computed using the formulas for a normal distribution, and
the empirical distribution is then compared with a normal distribution.
b
a
Fig. 3.8 a
Probability density function
f
(
x
), and
b
cumulative distribution function
F
(
x
), of a
logarithmic normal distribution with a mean ʼ=0 and with various values for ˃.