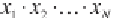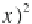Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
h e average growth of these values is 1.3006 suggesting an approximate per
annum growth in the population of 30%. h e arithmetic mean would result
in an erroneous value of 1.3167 or approximately 32% annual growth. h e
geometric mean is also a useful measure of central tendency for skewed or
log-normally distributed data, in which the logarithms of the observations
follow a Gaussian or normal distribution. h e geometric mean, however, is
not used for data sets containing negative values. Finally, the
harmonic mean
is also used to derive a mean value for asymmetric or log-normally
distributed data, as is the geometric mean, but neither is robust to outliers.
h e harmonic mean is a better average when the numbers are dei ned in
relation to a particular unit. h e commonly quoted example is for averaging
velocities. h e harmonic mean is also used to calculate the mean of sample
sizes.
Measures of Dispersion
Another important property of a distribution is the dispersion. Some of the
parameters that can be used to quantify dispersion are illustrated in Figure
3.3. h e simplest way to describe the dispersion of a data set is by the
range
,
which is the dif erence between the highest and lowest value in the data set,
given by
Since the range is dei ned by the two extreme data points it is very susceptible
to outliers and hence it is not a reliable measure of dispersion in most cases.
Using the interquartile range of the data, i.e., the middle 50% of the data,
attempts to overcome this problem.
A more useful measure for dispersion is the
standard deviation
.