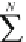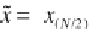Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
b
a
Fig. 3.1
Graphical representation of an empirical frequency distribution.
a
In a
histogram
,
the frequencies are organized in
nbin
classes and plotted as a bar plot.
b
h e
cumulative
distribution plot
of a frequency distribution displays the totals of all observations lower than
and equal to a certain value. h is plot is normalized to a total number of observations of one.
that describes the data. h e most popular indicator of central tendency is the
arithmetic mean
, which is the sum of all data points divided by the number
of observations:
h e arithmetic mean can also be called the mean or the average of a univariate
data set. h e sample mean is used as an estimate of the population mean ʼ
for the underlying theoretical distribution. h e arithmetic mean is, however,
sensitive to outliers, i.e., extreme values that may be very dif erent from the
majority of the data, and the
median
is therefore ot en used as an alternative
measure of central tendency. h e median is the
x
-value that is in the middle
of the data set, i.e., 50% of the observations are smaller than the median and
50% are larger. h e median of a data set sorted in ascending order is dei ned
as
if
N
is odd and