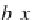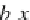Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 9.7
Cluster analysis output. h e dendrogram shows clear groups consisting of samples 1,
2, 8, 9 and 10 (the magmatic source rocks), samples 3, 4 and 5 (the magmatic dyke containing
ore minerals), and samples 6 and 7 (the sandstone unit).
ans =
0.7579
h e result is convincing since the closer this coei cient is to one, the better
the cluster solution.
9.6 Multiple Linear Regression
In Chapter 4 linear regression models were introduced as a way of describing
the relationship between a dependent variable
y
and an independent variable
x
. h e dependent variable is also known as the
response variable
, and the
independent variable as the
predictor variable
. A multiple linear regression
model describes the relationship between a dependent (or response) variable
y
, and
n
independent (or predictor) variables
x
i
where
b
i
are the
n
+1 regression coei cients of the linear model. h e linearity
in the term multiple linear regression refers to the fact that the response
variable is a linear function of the predictor variables. h e regression
coei cients are estimated by minimizing the mean-squared dif erence
between the predicted and true values of the response variable
y
. As an
example that is commonly used in the earth sciences is the quality of crude
oil, which is assumed to be linearly dependent on the age of the sediment, the