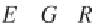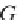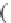Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
For kriging we must minimize this equation (a quadratic objective
function), satisfying the condition that the sum of the weights should be
equal to one (linear constraint). h is optimization problem can be solved
using a Lagrange multiplier ʽ, resulting in a
linear kriging system
of
N
+1
equations and
N
+1 unknowns:
At er obtaining the weights ʻ
i
, the kriging variance is given by
h e kriging system can be presented in a matrix notation:
where
is the matrix of the coei cients: these are the modeled variogram values for
the pairs of observations. Note that on the diagonal of the matrix, where
separation distance is zero, the value of ʳ disappears.
is the vector of the unknown weights and the Lagrange multiplier.