Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
d
c
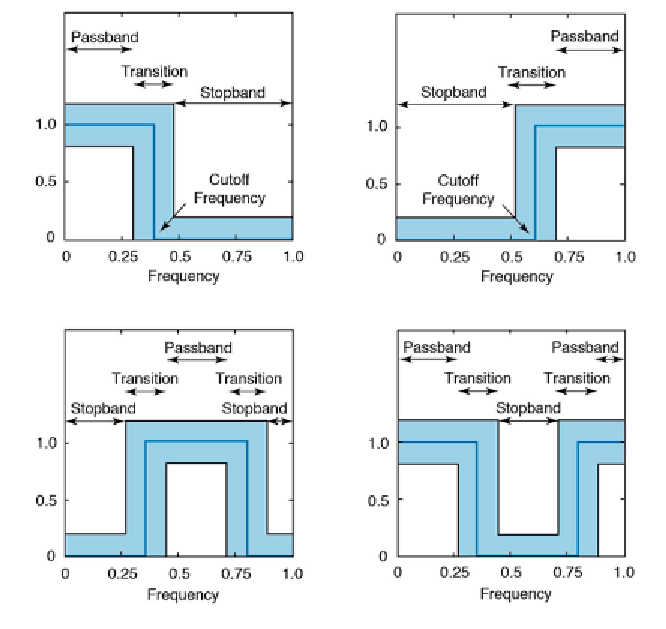
Fig. 6.5
Frequency responses for the fundamental types of frequency-selective i lters.
a
Lowpass i lter to suppress the high-frequency component of a signal. In earth sciences, such
i lters are ot en used to suppress high-frequency noise in a low-frequency signal.
b
Highpass
i lters to remove all low frequencies and trends in natural data.
c-d
Bandpass and bandstop
i lters to extract or suppress a certain frequency band. h e solid line in all graphics depicts
the ideal frequency response of a frequency-selective i lter, while the gray band shows the
tolerance for a low-order design of such a i lter. In practice, the frequency response lies within
the gray band.
frequency, which in our example is 0.5 (i.e., half of the sampling frequency).
h e outputs from
butter
are the i lter weights
a12
and
b12
.
[b12,a12] = butter(5,0.1/0.5);
h e frequency characteristics of the i lter show a relatively smooth transition
from the passband to the stopband, but the advantage of the i lter is its low
order.
[h,w] = freqz(b12,a12,1024);