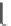Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
xlabel('Delay'), ylabel('Autocorrelation')
grid on
We now choose a delay such that the autocorrelation function for the i rst
time period equals zero. In our case this is i ve, which is the value that we have
already used in our example of phase space reconstruction. h e appropriate
embedding dimension can be estimated using the false nearest neighbors
method, or more simple, using recurrence plots, which are introduced in the
next subsection. h e embedding dimension is gradually increased until the
majority of the diagonal lines are parallel to the line of identity.
h e phase space trajectory or its reconstruction is the basis of several
measures defined in nonlinear data analysis, such as
Lyapunov exponents
,
Rényi entropies
, or
dimensions
. h e topic on nonlinear data analysis by Kantz
and Schreiber (1997) is recommended for more detailed information on
these methods. Phase space trajectories or their reconstructions are also
necessary for constructing recurrence plots.
Recurrence Plots
h e phase space trajectories of dynamic systems that have more than three
dimensions are dii cult to portray visually.
Recurrence plots
provide a way
of analyzing systems with higher dimensions. h ey can be used, e.g., to
detect transitions between dif erent regimes, or to detect interrelationships
or synchronisations between dif erent systems (Marwan 2007). h e method
was i rst introduced by Eckmann and others (1987). h e recurrence plot is a
tool that displays the recurrences of states in the phase space through a two-
dimensional plot.
If the distance between two states,
i
and
j
, on the trajectory is smaller than
a given threshold ʵ, the value of the recurrence matrix
R
is one; otherwise it
is zero. h is analysis is therefore a pairwise test of all states. For
N
states we
compute
N
2
tests. h e recurrence plot is then the two-dimensional display
of the
N
-by-
N
matrix, where black pixels represent
R
i,j
=1 and white pixels
indicate
R
i,j
=0, with a coordinate system representing two time axes. Such
recurrence plots can help to i nd a preliminary characterization of the
dynamics of a system or to i nd transitions and interrelationships within a
system (cf. Fig. 5.22).