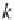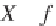Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
h e cross-covariance series again depends on the amplitudes of
x
(
t
) and
y
(
t
).
Normalizing the covariance by the standard deviations of
x
(
t
) and
y
(
t
) yields
the cross-correlation sequence.
h e
Blackman-Tukey method
uses the complex Fourier transform
X
xy
(
f
) of
the cross-correlation sequence
corr
xy
(
k
)
where
M
is the maximum lag and
f
s
the sampling frequency. h e absolute
value of the complex Fourier transform
X
xy
(
f
) is the cross-spectrum while
the angle of
X
xy
(
f
) represents the phase spectrum. h e phase dif erence is
important in calculating leads and lags between two signals, a parameter
ot en used to propose causalities between two processes documented by the
signals. h e correlation between two spectra can be calculated by means of
the coherence:
h e coherence is a real number between 0 and 1, where 0 indicates no
correlation and 1 indicates maximum correlation between
x
(
t
) and
y
(
t
) at the
frequency
f
. A signii cant degree of coherence is an important precondition
for computing phase shit s between two signals.
5.4 Examples of Auto-Spectral and Cross-Spectral Analysis
h e Signal Processing Toolbox provides numerous methods for computing
spectral estimators for time series. h e introduction of object-oriented
programming with MATLAB has led to the launch of a new set of functions
performing spectral analyses. Type
help
spectrum
for more information
about object-oriented spectral analysis. h e non-object-oriented functions
to perform spectral analyses, however, are still available. One of the oldest
functions in this toolbox is
periodogram(x,window,nfft,fs)
which computes
the power spectral density
Pxx
of a time series
x(t)
using the periodogram