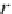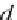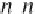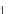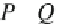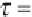Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
non-parametric measure of correlation (Spearman 1904, 1910). Furthermore,
since it uses the ranks of the values in
x
and
y
rather than their numerical
values, it can be used to i nd correlations in nonlinear data, and even in non-
numerical data such as fossil names or rock types in stratigraphic sequences.
Having replaced the numerical values in
x
and
y
by their ranks (whereby
multiple values in
x
and
y
are replaced by their respective average ranks) the
sample Spearman's rank correlation coei cient is dei ned as
where
d
i
is the dif erence between the ranks of the two variables. Since this
correlation coei cient is based on ranks rather than numerical values it is
less sensitive to outliers than Pearson's correlation coei cient.
Another alternative to Pearson's correlation coei cient is the
Kendall's
tau rank correlation coei cient
proposed by the British statistician Maurice
Kendall (1907-1983). h is is also a non-parametric measure of correlation,
similar to the Spearman's rank correlation coei cient (Kendall 1938). h e
Kendall's tau rank correlation coei cient compares the ranks of the numerical
values in
x
and
y
, which means a total of 0.5
n
(
n
-1) pairs to compare. Pairs
of observations (
x
i
,
y
i
) and (
x
j
,
y
j
) are said to be concordant if the ranks for
both observations are the same, and discordant if they are not. h e sample
Kendall's tau rank correlation coei cient is dei ned as
where
P
is the number of concordant pairs and
Q
is the number of discordant
pairs. Kendall's correlation coei cient typically has a lower value than Spear-
man's correlation coei cient.
h e following example illustrates the use of the correlation coei cients
and highlights the potential pitfalls when using these measures of linear
trends. It also describes the resampling methods that can be used to explore
the coni dence level of the estimate for ˁ. h e synthetic data consist of two
variables, the age of a sediment in kiloyears before present and the depth
below the sediment-water interface in meters. h e use of synthetic data sets
has the advantage that we fully understand the linear model behind the data.
h e data are represented as two columns contained in i le
agedepth_1.