Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
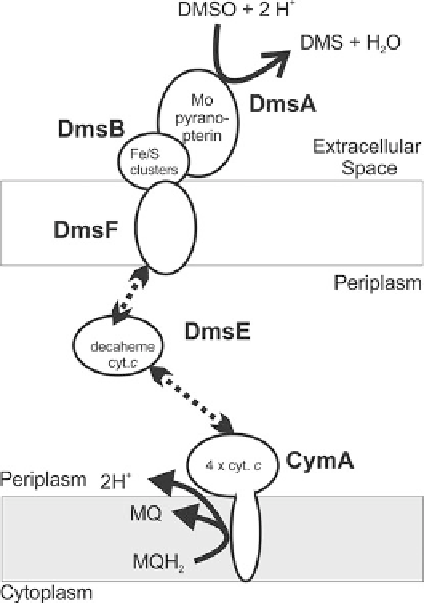
2.1.3.3 Extracellular Dimethylsulfoxide Reduction
in
Shewanella oneidensis
The DMSO respiration system of
Shewanella oneidensis
is a special case as it is
located in the outer membrane rather than in the periplasmic space (Figure
7
). The
core catalytic subunits of this complex, DmsA and DmsB, have high homology to
the
E. coli
DMSO reductase, but homologues of the DmsC membrane anchor
protein are absent from the
S. oneidensis
genome [
165
]. Instead, the two
S. oneidensis
gene clusters (SO_1427-SO_1432,
dmsEFABGH
; SO_4362-
SO_4357) encoding DmsAB-related protein complexes encode homologues of
proteins involved in metal reduction, MtrAB ('DmsEF' in the
Shewanella
DMSO
reductase complex), that can mediate outer membrane attachment and electron
transfer across the bacterial periplasm as well as a molecular chaperone ('DmsG')
and an 'accessory protein' ('DmsH') of 155 aa. Within the second gene cluster, the
dmsGH
homologous genes are located upstream of the
mtrAB
related genes.
Figure 7 Structure and
cellular organization of the
Shewanella oneidensis
outer membrane DMSO
reductase in the bacterial
cell envelope. MQ/MQH
2
,
menaquinone/menaquinol;
cyt.
c
, cytochrome
c
; broken
arrows indicate transient
protein interactions.
Only the
dmsEFABGH
(SO_1427-SO_1432) operon shows significant induction
during anaerobic growth and was shown by mutagenesis studies to be the main
DMSO respiratory gene cluster in
S. oneidensis
[
166
]
.
Electron transfer to the
DMSO reductase complex requires menaquinone as the electron donor, and pro-
ceeds via
the CymA membrane-bound tetraheme
cytochrome
and the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search