Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
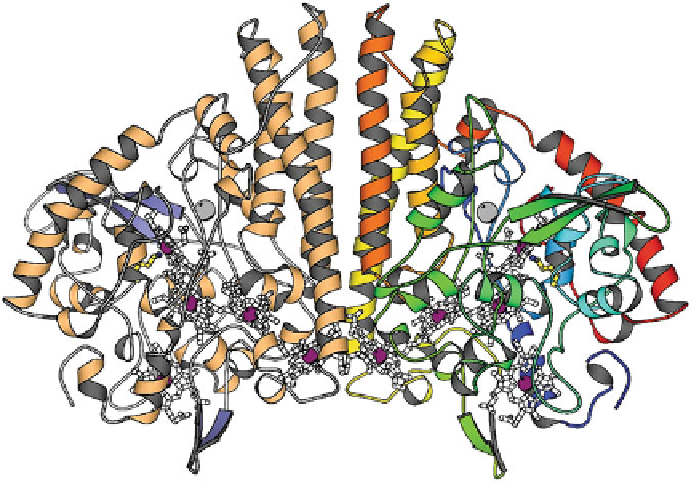
Figure 3 Three-dimensional structure of the cytochrome
c
nitrite reductase (NrfA) dimer from
Sulfurospirillum deleyianum
. A front view with the dimer axis oriented vertically, the five hemes
in each monomer (white), the Ca
2+
ions (grey), and residue Lys133 which coordinates the active
site iron atom (yellow). In the right monomer, the protein chain is colored blue from the amino-
terminal end to red at the carboxy-terminal end, in the left mono-mer according to secondary
structure. The dimer interface is dominated by three long
-helices per monomer. All hemes in the
dimer are covalently attached to the protein. Taken by permission from [
58
]; copyright 1999
Nature Publishing Group. PDB code: 1QDB.
ʱ
thought to interact with the membrane-bound tetraheme cytochrome
c
CymA
(see Section
4.3
)[
64
].
The NrfA protein binds five
c
-type heme groups via thioether bonds to the
cysteines of conserved heme
c
attachment motifs (Figures
2
and
4
), four of them
with the
classical
Cys-X-X-Cys-His and one with the Cys-X-X-Cys-Lys sequence.
Thus, in most known NrfA proteins, all heme irons are bis-histidinyl-coordinated
(hemes 2-4, sp
2
-N
imidazole
) except for the catalytic center (heme 1), which is
bound to a lysine as the 5th coordinate ligand (sp
3
-NH
2
) of an unprecedented
structural motif. A minority of known NrfA sequences, however, contained five
Cys-X-X-Cys-His heme
c
binding motifs, such as the enzyme from
Campylobacter
jejuni
which was shown to catalyze nitrite reduction at a high specific activity
(enzyme class 2.2 in Table
1
)[
65
].
A recent phylogenetic analysis of 272 full-length NrfA protein sequences
distinguished 18 NrfA clades with robust statistical support [
44
]. Three clades
possessed a Cys-X-X-Cys-His motif in the first heme-binding domain with repre-
sentative organisms being classified in a surprisingly diverse range of bacterial
phyla such as Proteobacteria (delta and epsilon classes), Planctomycetes,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search