Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
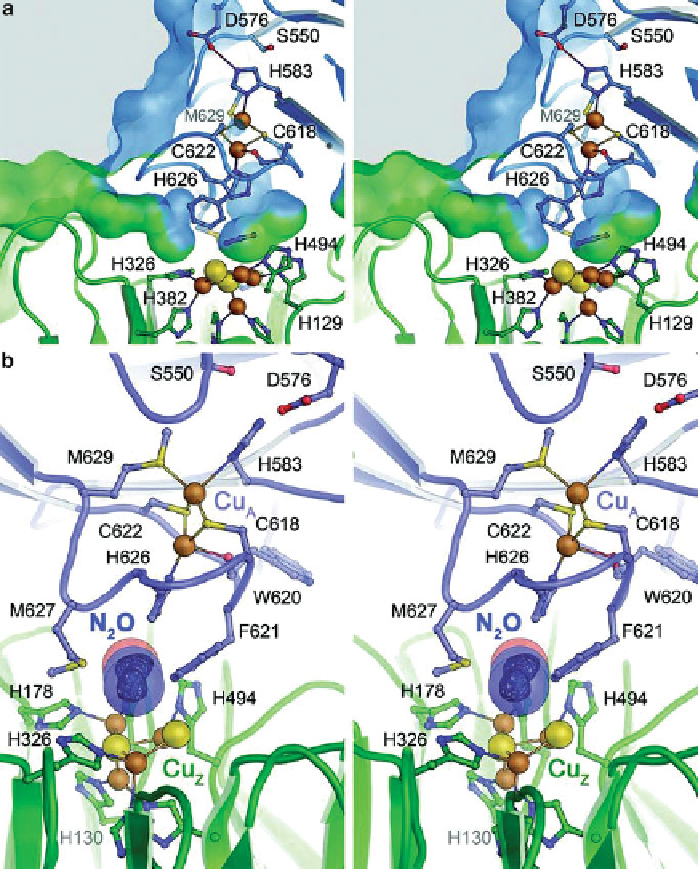
Figure 9 Substrate access and N
2
O binding at the active site of N
2
O reductase. (a) Stereo
representation of the molecular surface at the interface between the cupredoxin domain (blue)
and the
ʲ
-propeller domain with the active site situated below. Substrate access is provided
via
a
hydrophic channel along the domain interface, leading to a vestibule close to Cu
Z
. The access to
the N
2
O binding site on Cu
Z
is controlled by residues Phe621 and Met627. (b) Observed binding of
N
2
O between Cu
A
and Cu
Z
in gas-pressurized crystals of
P. stutzeri
N
2
OR form I (PDB ID 3SBR).
A difference electron density map for the substrate is shown below a transparent van-der-Waals
surface. Upon N
2
O binding, residue His583 at Cu
A
was invariably found to coordinate to
the nearby copper ion (Figure
6
). The positioning of the substrate between the two metal sites
suggests that electron transfer might occur directly from Cu
A
to N
2
O, rather than involving a
reduction of Cu
Z
.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search