Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
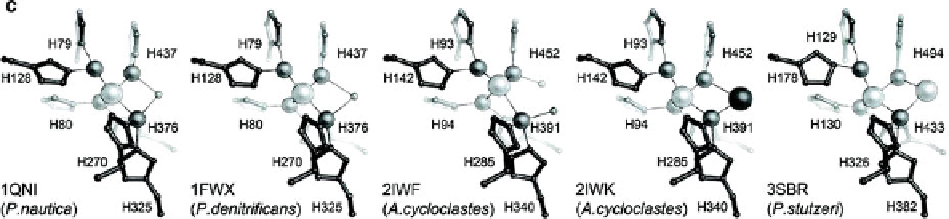
Figure 7 Cu
Z
, the catalytic center of N
2
O reductase. (a) The tetranuclear Cu
Z
site is located at the hub of the N-terminal
ʲ
-propeller domain. It constitutes a
unique [4Cu:2S] cluster coordinated to seven histidine residues. (b) The spectroscopically and functionally distinct forms Cu
Z
(above) and Cu
Z
* (below) differ
in the presence of the second sulfur atom in the cluster. While Cu
Z
undergoes a redox transition from a [2Cu
+
:2Cu
2+
] state to a [3Cu
+
:1Cu
2+
] and cannot be
further reduced, Cu
Z
* is isolated as [3Cu
+
:1Cu
2+
] and can be further reduced to a [4Cu
+
] state by sodium dithionite and methyl viologen. (c) The variation of
Cu
Z
structures from different crystal structures of nitrous oxide reductases. The first structures (PDB ID 1QNI, 1FWX) showed mixtures of Cu
Z
and Cu
Z
*,
where a partially occupied sulfur atom between Cu
1
and Cu
4
was interpreted as a bridging water or hydroxo species. A form II structure (PDB ID 2IWF) then
had two water ligands at the Cu
1
-Cu
4
edge, but would bind the inhibitor iodide in a bridging fashion (PDB ID 1IWK). Only in the purple form I structure (PDB
3SBR), Cu
Z
was in the complete [4Cu:2S] state.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search