Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
use the D-cluster which may become obstructed or held too far from the electrode,
but instead enter the catalytic cycle at a higher potential than with CODH I
Ch
or
CODH II
Ch
. The reducing power is thus dissipated and electron transfer to the
C-cluster becomes an unfavorable step.
To identify whether ACS influences the performance of CODH, an experiment was
performed in which several chemical reagents, such as sodium dodecyl sulfate (which
separates CODH and ACS partially), 1,10-phenanthroline, (which inhibits the active
site in ACS), and acetyl-CoA (the product of the reaction carried out by CODH/
ACS
Mt
) were added [
53
-
55
]. However, an electrocatalytic current due to CO
2
reduc-
tion was still not observed, so this observation remains a puzzle. The turnover
frequency for CO
2
reduction by CODH/ACS
Mt
is normally determined by measuring
the CO product binding to hemoglobin and a rate constant of approximately 1.3 s
1
was reported [
56
]. However, several studies have led to the picture that during
synthesis of acetyl-CoA, CO arising from reduction of CO
2
diffuses through a channel
in the enzyme complex to reach the A-cluster without escaping [
57
,
58
].
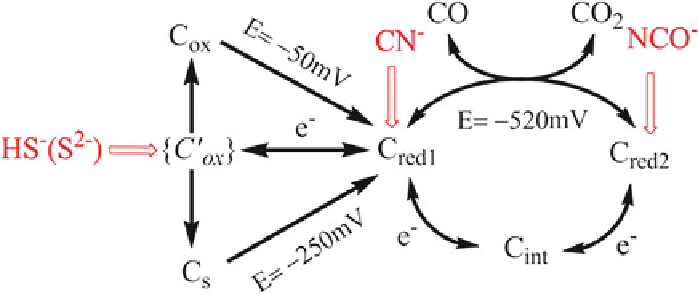
5 Potential-Dependent Reactions with Inhibitors
The catalytic current provides an important observable (commonly called a 'han-
dle') for investigating the kinetics and potential dependence of the reactions with
inhibitors, at a level of kinetic detail that is difficult to achieve by conventional
methods. Some of the opportunities for inhibitors to bind are shown in Scheme
1
and elaborated upon (in an electrochemical sense) in Scheme
2
. Protein film
electrochemistry is able to reveal and clarify the different ways that these small
molecules interrupt catalysis. We will discuss next how cyanide, isoelectronic with
CO, mainly inhibits CO oxidation, whereas cyanate, isoelectronic with CO
2
, targets
CO
2
reduction. Sulfide is also an inhibitor but is unusual because it acts only under
oxidizing conditions. Thiocyanate (SCN
) is also considered.
Scheme 2 Summary of the interceptions of the catalytic cycle of CODH by small molecule
inhibitors. The potential -520 mV is the standard potential for the CO
2
/CO half cell reaction at
pH 7.0. The potentials -50 mV and -250 mV are the values observed for re-activation of CODH I
with and without sulfide. Reprinted with permission from [
18
]; copyright 2013 American Chem-
ical Society.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search