Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
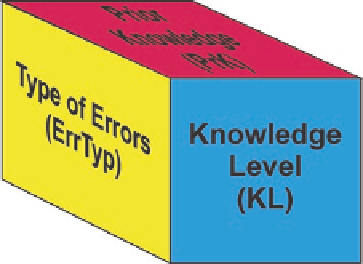
Fig. 3.4
The three-
dimensional stereotype model
the learner reads, if s/he has difficulties in understanding, if s/he is careless, if s/he
has confused with a prior knowledge on a related concept etc. Finally, the third
dimension (PrK) concerns prior knowledge of the student on related knowledge
domain fields. In this way, the tutoring system is able to distinguish if an error
occurs due to non-learning or due to affecting by prior knowledge.
The stereotypes are updated each time new information about the learner
is required. New information about the learner is obtained each time s/he inter-
acts with the system. More concretely, each time the learner interacts with the
system, s/he takes a test, the results of which determine the learner's knowledge
and update her/his overlay model. The first dimension of the stereotype student
model receives information from the overlay model and determines the value of
KL. The stereotype categories of the second and third dimension, to which the
learner should be classified, are not affected by the information that is received by
the overlay model. The stereotype category of the second dimension to which the
learner belongs each time, is determined by the type of errors that s/he does dur-
ing the test. Also, the third dimension is determined by the learner during her/his
registration to the system.
3.4 Operation of F.O.S.
When the learner interacts with the system for the first time, s/he asked to enter
static information like her/his age, name and the prior knowledge (PrK) that
s/he has on related fields with the knowledge domain of the system. Initially,
s/he is considered to be novice. After that, the student model is updated each
time new information about the learner is required. New information about the
learner is obtained each time s/he interacts with the system. More concretely,
each time the learner interacts with the system, s/he takes a test, the results of
which determine the learner's knowledge and errors and update her/his over-
lay model. In particular, each time the learner interacts with the system, s/he
reads a domain concept Ci
i
and takes a test to assess her/his knowledge on the
particular domain concept. The results of the test determine either the learner's
Search WWH ::

Custom Search